Synergistic Role of Temperature and Salinity in Aggregation of Nonionic Surfactant-Coated Silica Nanoparticles
- PMID: 37053432
- PMCID: PMC10134496
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c00432
Synergistic Role of Temperature and Salinity in Aggregation of Nonionic Surfactant-Coated Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
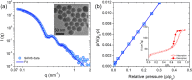
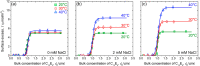
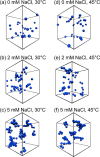
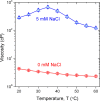
The adsorption of nonionic surfactants onto hydrophilic nanoparticles (NPs) is anticipated to increase their stability in aqueous medium. While nonionic surfactants show salinity- and temperature-dependent bulk phase behavior in water, the effects of these two solvent parameters on surfactant adsorption and self-assembly onto NPs are poorly understood. In this study, we combine adsorption isotherms, dispersion transmittance, and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) to investigate the effects of salinity and temperature on the adsorption of pentaethylene glycol monododecyl ether (C12E5) surfactant on silica NPs. We find an increase in the amount of surfactant adsorbed onto the NPs with increasing temperature and salinity. Based on SANS measurements and corresponding analysis using computational reverse-engineering analysis of scattering experiments (CREASE), we show that the increase in salinity and temperature results in the aggregation of silica NPs. We further demonstrate the non-monotonic changes in viscosity for the C12E5-silica NP mixture with increasing temperature and salinity and correlate the observations to the aggregated state of NPs. The study provides a fundamental understanding of the configuration and phase transition of the surfactant-coated NPs and presents a strategy to manipulate the viscosity of such dispersion using temperature as a stimulus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A coarse-grain molecular dynamics study of oil-water interfaces in the presence of silica nanoparticles and nonionic surfactants.J Chem Phys. 2017 May 28;146(20):204702. doi: 10.1063/1.4984073. J Chem Phys. 2017. PMID: 28571351 Free PMC article.
-
Solubilization of polyelectrolytic hairy-rod polyfluorene in aqueous solutions of nonionic surfactant.J Phys Chem B. 2006 Jun 1;110(21):10248-57. doi: 10.1021/jp0560563. J Phys Chem B. 2006. PMID: 16722726
-
Probing the adsorption of nonionic micelles on different-sized nanoparticles by scattering techniques.Phys Rev E. 2020 Dec;102(6-1):062601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.102.062601. Phys Rev E. 2020. PMID: 33465948
-
Adsorption of nonionic surfactant on silica nanoparticles: structure and resultant interparticle interactions.J Phys Chem B. 2010 Sep 2;114(34):10986-94. doi: 10.1021/jp1033799. J Phys Chem B. 2010. PMID: 20687569
-
A review on experimental studies of surfactant adsorption at the hydrophilic solid-water interface.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2004 Aug 31;110(3):75-95. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2004.03.001. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2004. PMID: 15328059 Review.
Cited by
-
Parabolic Viscosity Behavior of NaCl-Thickened Surfactant Systems upon Temperature Change.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 26;8(40):37511-37520. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05855. eCollection 2023 Oct 10. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37841189 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Reverse Engineering Analysis of the Scattering Experiment Method for Interpretation of 2D Small-Angle Scattering Profiles (CREASE-2D).JACS Au. 2024 Mar 20;4(4):1570-1582. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.4c00068. eCollection 2024 Apr 22. JACS Au. 2024. PMID: 38665659 Free PMC article.
-
Surface Science View of Perfluoroalkyl Acids (PFAAs) in the Environment.ACS Environ Au. 2024 Apr 30;4(4):173-185. doi: 10.1021/acsenvironau.3c00079. eCollection 2024 Jul 17. ACS Environ Au. 2024. PMID: 39035868 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bharti B.; Meissner J.; Gasser U.; Findenegg G. H. Surfactant Adsorption and Aggregate Structure at Silica Nanoparticles: Effects of Particle Size and Surface Modification. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 6573–6581. 10.1039/c2sm25648g. - DOI
-
- Binks B. P.; Kirkland M.; Rodrigues J. A. Origin of Stabilisation of Aqueous Foams in Nanoparticle-Surfactant Mixtures. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 2373–2382. 10.1039/b811291f. - DOI
-
- Fameau A. L.; Salonen A. Effect of Particles and Aggregated Structures on the Foam Stability and Aging. Comptes Rendus Phys 2014, 15, 748–760. 10.1016/j.crhy.2014.09.009. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

