Post-translational modifications of histone proteins by monoamine neurotransmitters
- PMID: 37054563
- PMCID: PMC10225327
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2023.102302
Post-translational modifications of histone proteins by monoamine neurotransmitters
Abstract
Protein monoaminylation is a biochemical process through which biogenic monoamines (e.g., serotonin, dopamine, histamine, etc.) are covalently bonded to certain protein substrates via Transglutaminase 2, an enzyme that catalyzes the transamidation of primary amines to the γ-carboxamides of glutamine residues. Since their initial discovery, these unusual post-translational modifications have been implicated in a wide variety of biological processes, ranging from protein coagulation to platelet activation and G-protein signaling. More recently, histone proteins - specifically histone H3 at glutamine 5 (H3Q5) - have been added to the growing list of monoaminyl substrates in vivo, with H3Q5 monoaminylation demonstrated to regulate permissive gene expression in cells. Such phenomena have further been shown to contribute critically to various aspects of (mal)adaptive neuronal plasticity and behavior. In this short review, we examine the evolution of our understanding of protein monoaminylation events, highlighting recent advances in the elucidation of their roles as important chromatin regulators.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

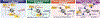
References
-
- Fukumoto T, Kema IP, Levin M. Serotonin signaling is a very early step in patterning of the left-right axis in chick and frog embryos. Current Biology. 2005;15(9):794–803. - PubMed
-
- Buznikov GA, Lambert WH, Lauder JM. Serotonin and serotonin-like substances as regulators of early embryogenesis and morphogenesis. Cell and Tissue Research. 2001;305(2):177–86. - PubMed
-
- Azmitia EC. Modern views on an ancient chemical: Serotonin effects on cell proliferation, maturation, and apoptosis. In: Brain Research Bulletin. 2001. p. 413–24. - PubMed
-
- Young AB, Pert CD, Brown DG, Taylor KM, Snyder SH. Nuclear localization of histamine in neonatal rat brain. Science. 1971;173(3993):247–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

