Effect of SAM junctional tourniquet on respiration when applied in the axilla: A swine model
- PMID: 37055266
- PMCID: PMC10244247
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2023.03.005
Effect of SAM junctional tourniquet on respiration when applied in the axilla: A swine model
Abstract
Purpose: SAM junctional tourniquet (SJT) has been applied to control junctional hemorrhage. However, there is limited information about its safety and efficacy when applied in the axilla. This study aims to investigate the effect of SJT on respiration when used in the axilla in a swine model.
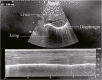
Methods: Eighteen male Yorkshire swines, aged 6-month-old and weighing 55 - 72 kg, were randomized into 3 groups, with 6 in each. An axillary hemorrhage model was established by cutting a 2 mm transverse incision in the axillary artery. Hemorrhagic shock was induced by exsanguinating through the left carotid artery to achieve a controlled volume reduction of 30% of total blood volume. Vascular blocking bands were used to temporarily control axillary hemorrhage before SJT was applied. In Group I, the swine spontaneously breathed, while SJT was applied for 2 h with a pressure of 210 mmHg. In Group II, the swine were mechanically ventilated, and SJT was applied for the same duration and pressure as Group I. In Group III, the swine spontaneously breathed, but the axillary hemorrhage was controlled using vascular blocking bands without SJT compression. The amount of free blood loss was calculated in the axillary wound during the 2 h of hemostasis by SJT application or vascular blocking bands. After then, a temporary vascular shunt was performed in the 3 groups to achieve resuscitation. Pathophysiologic state of each swine was monitored for 1 h with an infusion of 400 mL of autologous whole blood and 500 mL of lactated ringer solution. Tb and T0 represent the time points before and immediate after the 30% volume-controlled hemorrhagic shock, respectively. T30, T60, T90 and T120, denote 30, 60, 90, and 120 min after T0 (hemostasis period), while T150, and T180 denote 150 and 180 min after T0 (resuscitation period). The mean arterial pressure and heart rate were monitored through the right carotid artery catheter. Blood samples were collected at each time point for the analysis of blood gas, complete cell count, serum chemistry, standard coagulation tests, etc., and thromboelastography was conducted subsequently. Movement of the left hemidiaphragm was measured by ultrasonography at Tb and T0 to assess respiration. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed using repeated measures of two-way analysis of variance with pairwise comparisons adjusted using the Bonferroni method. All statistical analyses were processed using GraphPad Prism software.
Results: Compared to Tb, a statistically significant increase in the left hemidiaphragm movement at T0 was observed in Groups I and II (both p < 0.001). In Group III, the left hemidiaphragm movement remained unchanged (p = 0.660). Compared to Group I, mechanical ventilation in Group II significantly alleviated the effect of SJT application on the left hemidiaphragm movement (p < 0.001). Blood pressure and heart rate rapidly increased at T0 in all three groups. Respiratory arrest suddenly occurred in Group I after T120, which required immediate manual respiratory assistance. PaO2 in Group I decreased significantly at T120, accompanied by an increase in PaCO2 (both p < 0.001 vs. Groups II and III). Other biochemical metabolic changes were similar among groups. However, in all 3 groups, lactate and potassium increased immediately after 1 min of resuscitation concurrent with a drop in pH. The swine in Group I exhibited the most severe hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis. The coagulation function test did not show statistically significant differences among three groups at any time point. However, D-dimer levels showed a more than 16-fold increase from T120 to T180 in all groups.
Conclusion: In the swine model, SJT is effective in controlling axillary hemorrhage during both spontaneous breathing and mechanical ventilation. Mechanical ventilation is found to alleviate the restrictive effect of SJT on thoracic movement without affecting hemostatic efficiency. Therefore, mechanical ventilation could be necessary before SJT removal.
Keywords: Axilla; Junctional hemorrhage; Respiration; Swine model; Tourniquet.
Copyright © 2023 Chinese Medical Association. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Physiological Consequences of Abdominal Aortic and Junctional Tourniquet (AAJT) Application to Control Hemorrhage in a Swine Model.Shock. 2016 Sep;46(3 Suppl 1):160-6. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000651. Shock. 2016. PMID: 27172149
-
Safety and Effectiveness Evidence of SAM(r) Junctional Tourniquet to Control Inguinal Hemorrhage in a Perfused Cadaver Model.J Spec Oper Med. 2014 Summer;14(2):21-25. doi: 10.55460/D5PS-NYQA. J Spec Oper Med. 2014. PMID: 24952036
-
Combined effect of intermittent hemostasis and a modified external hemorrhage control device in a lethal swine model.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 30;10(17):e37017. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37017. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39296135 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of junctional tourniquets: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2019 Mar;86(3):532-539. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000002159. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2019. PMID: 30507857
-
Effects of increased oxygen breathing in a volume controlled hemorrhagic shock outcome model in rats.Resuscitation. 2000 Aug 1;45(3):209-20. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9572(00)00183-0. Resuscitation. 2000. PMID: 10959021 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress of tourniquets and their application in the Russia-Ukraine Conflict.Chin J Traumatol. 2025 Jan;28(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2024.07.010. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Chin J Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 39542779 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
