Factors Associated With Failure of Health System Reform: A Systematic Review and Meta-synthesis
- PMID: 37055355
- PMCID: PMC10111098
- DOI: 10.3961/jpmph.22.394
Factors Associated With Failure of Health System Reform: A Systematic Review and Meta-synthesis
Abstract
Objectives: The health system reform process is highly political and controversial, and in most cases, it fails to realize its intended goals. This study was conducted to synthesize factors underlying the failure of health system reforms.
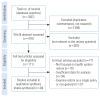
Methods: In this systematic review and meta-synthesis, we searched 9 international and regional databases to identify qualitative and mixed-methods studies published up to December 2019. Using thematic synthesis, we analyzed the data. We utilized the Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research checklist for quality assessment.
Results: After application of the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 40 of 1837 articles were included in the content analysis. The identified factors were organized into 7 main themes and 32 sub-themes. The main themes included: (1) reforms initiators' attitudes and knowledge; (2) weakness of political support; (3) lack of interest group support; (4) insufficient comprehensiveness of the reform; (5) problems related to the implementation of the reform; (6) harmful consequences of reform implementation; and (7) the political, economic, cultural, and social conditions of the society in which the reform takes place.
Conclusions: Health system reform is a deep and extensive process, and shortcomings and weaknesses in each step have overcome health reform attempts in many countries. Awareness of these failure factors and appropriate responses to these issues can help policymakers properly plan and implement future reform programs and achieve the ultimate goals of reform: to improve the quantity and quality of health services and the health of society.
Keywords: Failure; Health care reform; Systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Evaluating mental health care and policy in Spain.J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2010 Jun;13(2):73-86. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2010. PMID: 20919594 Review.
-
Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 May 24;17(2):e1173. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1173. eCollection 2021 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 37131927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Managing the health care market in developing countries: prospects and problems.Health Policy Plan. 1994 Sep;9(3):237-51. doi: 10.1093/heapol/9.3.237. Health Policy Plan. 1994. PMID: 10137740 Review.
-
The blind spots of psychiatric reform in Greece.Psychiatriki. 2024 Jun 19;35(2):99-102. doi: 10.22365/jpsych.2024.009. Epub 2024 May 29. Psychiatriki. 2024. PMID: 38814270 English, Greek, Modern.
Cited by
-
Perceived outcomes of medical teaching institute reforms: insights from management, faculty, and administration in Pakistani tertiary health care.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Sep 13;24(1):1061. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11416-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 39272050 Free PMC article.
-
Role and promise of health policy and systems research in integrating rehabilitation into the health systems.Health Res Policy Syst. 2024 Oct 9;22(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12961-024-01235-2. Health Res Policy Syst. 2024. PMID: 39385210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of China's primary healthcare reforms on utilisation, payments and self-reported health: a quasi-experimental analysis of a middle-aged and older cohort 2011-2018.BMJ Public Health. 2025 Mar 23;3(1):e001595. doi: 10.1136/bmjph-2024-001595. eCollection 2025. BMJ Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40134540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cassels A. Health sector reform: key issues in less developed countries. J Int Dev. 1995;7(3):329–347. - PubMed
-
- Franco LM, Bennett S, Kanfer R. Health sector reform and public sector health worker motivation: a conceptual framework. Soc Sci Med. 2002;54(8):1255–1266. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal JR, Huebner J, Hedgecock J, Sehgal AR, Jung P, Simon SR. Medical students’ knowledge of the U.S. health care system and their preferences for curricular change: a national survey. Acad Med. 2005;80(5):484–488. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Health care systems in transition: Lithuania. 2000. [cited 2022 Mar 7]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/108334 .
-
- Oberlander J. Unfinished journey--a century of health care reform in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(7):585–590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources