Robust aversive effects of trace amine-associated receptor 1 activation in mice
- PMID: 37055488
- PMCID: PMC10425385
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-023-01578-4
Robust aversive effects of trace amine-associated receptor 1 activation in mice
Abstract
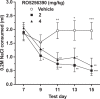
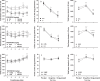
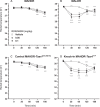
Drugs that stimulate the trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) are under clinical investigation as treatments for several neuropsychiatric disorders. Previous studies in a genetic mouse model of voluntary methamphetamine intake identified TAAR1, expressed by the Taar1 gene, as a critical mediator of aversive methamphetamine effects. Methamphetamine is a TAAR1 agonist, but also has actions at monoamine transporters. Whether exclusive activation of TAAR1 has aversive effects was not known at the time we conducted our studies. Mice were tested for aversive effects of the selective TAAR1 agonist, RO5256390, using taste and place conditioning procedures. Hypothermic and locomotor effects were also examined, based on prior evidence of TAAR1 mediation. Male and female mice of several genetic models were used, including lines selectively bred for high and low methamphetamine drinking, a knock-in line in which a mutant form of Taar1 that codes for a non-functional TAAR1 was replaced by the reference Taar1 allele that codes for functional TAAR1, and their matched control line. RO5256390 had robust aversive, hypothermic and locomotor suppressing effects that were found only in mice with functional TAAR1. Knock-in of the reference Taar1 allele rescued these phenotypes in a genetic model that normally lacks TAAR1 function. Our study provides important data on TAAR1 function in aversive, locomotor, and thermoregulatory effects that are important to consider when developing TAAR1 agonists as therapeutic drugs. Because other drugs can have similar consequences, potential additive effects should be carefully considered as these treatment agents are being developed.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 Regulation of Methamphetamine Intake and Related Traits.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Aug;40(9):2175-84. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.61. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25740289 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of TAAR1 function increases methamphetamine-induced excitability of dorsal raphe serotonin neurons and drives binge-level methamphetamine intake.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025 Jun;50(7):1136-1144. doi: 10.1038/s41386-025-02063-w. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39934409 Free PMC article.
-
A breeding strategy to identify modifiers of high genetic risk for methamphetamine intake.Genes Brain Behav. 2021 Feb;20(2):e12667. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12667. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Genes Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 32424970 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Treatment Targets in a Genetic Mouse Model of Voluntary Methamphetamine Drinking.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016;126:39-85. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27055611 Review.
-
An animal model of differential genetic risk for methamphetamine intake.Front Neurosci. 2015 Sep 23;9:327. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00327. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26441502 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Hidden Mark of a Troubled Past: Neuroimaging and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal Interactive Effects of Maternal Immune Activation and Adolescent THC Exposure Suggestive of Increased Neuropsychiatric Risk.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2025 Jan 23;5(3):100452. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2025.100452. eCollection 2025 May. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2025. PMID: 40115746 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation by Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 (TAAR1) of Dopaminergic-GABAergic Interaction in the Striatum: Effects of the Enhancer Drug (-)BPAP.Neurochem Res. 2025 Feb 4;50(2):94. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04337-7. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 39903411 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

