Inhibition of USP14 promotes TNFα-induced cell death in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)
- PMID: 37055579
- PMCID: PMC10154301
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-023-01144-x
Inhibition of USP14 promotes TNFα-induced cell death in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)
Abstract
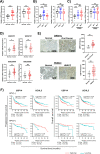
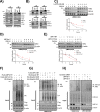
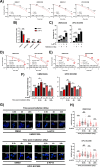
TNFα is a key mediator of immune, chemotherapy and radiotherapy-induced cytotoxicity, but several cancers, including head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC), display resistance to TNFα due to activation of the canonical NFκB pro-survival pathway. However, direct targeting of this pathway is associated with significant toxicity; thus, it is vital to identify novel mechanism(s) contributing to NFκB activation and TNFα resistance in cancer cells. Here, we demonstrate that the expression of proteasome-associated deubiquitinase USP14 is significantly increased in HNSCC and correlates with worse progression free survival in Human Papillomavirus (HPV)- HNSCC. Inhibition or depletion of USP14 inhibited the proliferation and survival of HNSCC cells. Further, USP14 inhibition reduced both basal and TNFα-inducible NFκB activity, NFκB-dependent gene expression and the nuclear translocation of the NFκB subunit RELA. Mechanistically, USP14 bound to both RELA and IκBα and reduced IκBα K48-ubiquitination leading to the degradation of IκBα, a critical inhibitor of the canonical NFκB pathway. Furthermore, we demonstrated that b-AP15, an inhibitor of USP14 and UCHL5, sensitized HNSCC cells to TNFα-mediated cell death, as well as radiation-induced cell death in vitro. Finally, b-AP15 delayed tumor growth and enhanced survival, both as a monotherapy and in combination with radiation, in HNSCC tumor xenograft models in vivo, which could be significantly attenuated by TNFα depletion. These data offer new insights into the activation of NFκB signaling in HNSCC and demonstrate that small molecule inhibitors targeting the ubiquitin pathway warrant further investigation as a novel therapeutic avenue to sensitize these cancers to TNFα- and radiation-induced cytotoxicity.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Burtness B, Rischin D, Greil R, Soulières D, Tahara M, Jr, de Castro G., Jr Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy for recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in KEYNOTE-048: subgroup analysis by programmed death ligand-1 combined positive score. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:2321–32. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02198. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

