Effect of intraoperative remimazolam on postoperative sleep quality in elderly patients after total joint arthroplasty: a randomized control trial
- PMID: 37055671
- PMCID: PMC10390348
- DOI: 10.1007/s00540-023-03193-5
Effect of intraoperative remimazolam on postoperative sleep quality in elderly patients after total joint arthroplasty: a randomized control trial
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the effect of intraoperative remimazolam sedation on postoperative sleep quality in elderly patients after total joint arthroplasty.
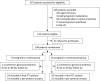
Methods: Between May 15, 2021 and March 26, 2022, 108 elderly patients (age ≥ 65 years) who received total joint arthroplasty under neuraxial anesthesia were randomized into remimazolam group (a loading dose of 0.025-0.1 mg/kg and followed by an infusion rate of 0.1-1.0 mg/kg/h till end of surgery) or routine group (sedation was given on patient's requirement by dexmedetomidine 0.2-0.7 μg/kg/h). Primary outcome was the subjective sleep quality at surgery night which was evaluated by Richards Campbell Sleep Questionnaire (RCSQ). Secondary outcomes included RCSQ scores at postoperative first and second nights and numeric rating scale pain intensity within first 3 days after surgery.
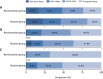
Results: RCSQ score at surgery night was 59 (28, 75) in remimazolam group which was comparable with 53 (28, 67) in routine group (median difference 6, 95% CI - 6 to 16, P = 0.315). After adjustment of confounders, preoperative high Pittsburg sleep quality index was associated worse RCSQ score (P = 0.032), but not remimazolam (P = 0.754). RCSQ score at postoperative first night [69 (56, 85) vs. 70 (54, 80), P = 0.472] and second night [80 (68, 87) vs. 76 (64, 84), P = 0.066] were equivalent between two groups. Safety outcomes were comparable between the two groups.
Conclusions: Intraoperative remimazolam did not significantly improve postoperative sleep quality in elderly patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty. But it is proved to be effective and safe for moderate sedation in these patients.
Clinical trial number and registry url: ChiCTR2000041286 ( www.chictr.org.cn ).
Keywords: Bispectral index; Remimazolam; Sedation; Sleep; Total joint arthroplasty.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Manning BT, Kearns SM, Bohl DD, Edmiston T, Sporer SM, Levine BR. Prospective assessment of sleep quality before and after primary total joint replacement. Orthopedics. 2017;40:e636–636e640. - PubMed
-
- Memtsoudis SG, Cozowicz C, Bekeris J, Bekere D, Liu J, Soffin EM, Mariano ER, Johnson RL, Hargett MJ, Lee BH, Wendel P. Anaesthetic care of patients undergoing primary hip and knee arthroplasty: consensus recommendations from the International Consensus on Anaesthesia-Related Outcomes after Surgery group (ICAROS) based on a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2019;123:269–287. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2019.05.042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

