Comparison between the long-axis in-plane and short-axis out-of-plane approaches for ultrasound-guided arterial cannulation: a meta-analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 37055775
- PMCID: PMC10100252
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-023-02076-2
Comparison between the long-axis in-plane and short-axis out-of-plane approaches for ultrasound-guided arterial cannulation: a meta-analysis and systematic review
Abstract
Background: The two most common methods for ultrasound-guided arterial cannulation are the long-axis in-plane (LA-IP) and short-axis out-of-plane (SA-OOP) approaches. However, it is uncertain which method is more advantageous. We conducted a meta-analysis of reported randomized clinical trials (RCTs) comparing the two techniques in terms of success rate, cannulation time, and complications.
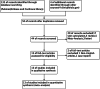
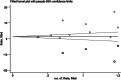
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library database for RCTs comparing the LA-IP and SA-OOP techniques for ultrasound-guided arterial cannulation published from inception through April 31, 2022. The Cochrane Collaboration's Risk of Bias Tool was used to evaluate the methodological quality of each RCT. Review Manager 5.4 and Stata/SE 17.0 were used to analyze the two primary outcome measures (first-attempt success rate and total success rate) and two secondary outcome measures (cannulation time and complications).
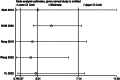
Results: A total of 13 RCTs with 1,377 patients were included. There were no significant differences in first-attempt success rate (risk ratio [RR], 0.93; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.78-1.12; P = 0.45; I2 = 84%) and overall success rate (RR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.95-1.02; P = 0.48; I2 = 57%). When compared with the LA-IP technique, the SA-OOP technique was associated with an increased incidence of posterior wall puncture (RR, 3.01; 95% CI, 1.27-7.14; P = 0.01; I2 = 79%) and hematoma (RR, 2.15; 95% CI, 1.05-4.37; P = 0.04; I2 = 63%). There was no significant difference in the incidence of vasospasm between techniques (RR, 1.26; 95% CI, 0.37-4.23; P = 0.07; I2 = 53%).
Conclusions: The present results suggest that the SA-OOP technique is associated with a higher incidence of posterior wall puncture and hematoma than the LA-IP technique, whereas success rates are similar for the two ultrasound-guided arterial cannulation techniques. These findings should be experimentally evaluated in a more rigorous manner due to high inter-RCT heterogeneity.
Keywords: Arterial cannulation; Long-axis in-plane; Meta-analysis; Short-axis out-of-plane; Ultrasound-guided.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





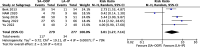
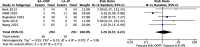



Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-guided radial arterial cannulation: long axis/in-plane versus short axis/out-of-plane approaches?J Clin Monit Comput. 2013 Jun;27(3):319-24. doi: 10.1007/s10877-013-9437-6. Epub 2013 Feb 16. J Clin Monit Comput. 2013. PMID: 23417581 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-axis in-plane combined with short-axis out-of-plane technique in ultrasound-guided arterial catheterization in infants: A randomized controlled trial.J Clin Anesth. 2023 May;85:111038. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2022.111038. Epub 2023 Jan 3. J Clin Anesth. 2023. PMID: 36603327 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison between the long-axis/in-plane and short-axis/out-of-plane approaches for ultrasound-guided vascular catheterization: an updated meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018 Feb 20;14:331-340. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S152908. eCollection 2018. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018. PMID: 29503552 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of out-of-plane short axis with in-plane long axis for ultrasound-guided radial arterial cannulation: A systematic review with trial sequential analysis of randomised controlled trials.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Oct 12;9:983532. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.983532. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36312257 Free PMC article.
-
[Short-axis versus long-axis approach in ultrasound-guided central venous cannulation: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020 Mar 30;40(3):308-315. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.03.02. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32376578 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Radial Arterial Cannulation by Ultrasound-Guided Dynamic Needle-Tip Positioning Using the Short-Axis Out-of-Plane Approach Versus the Long-Axis In-Plane Approach: A Randomized Controlled Study.Cureus. 2024 Feb 14;16(2):e54183. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54183. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38496072 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Vascular Access in Infants: Is Ultrasound-Guided Cannulation More Effective than the Conventional Approach? A Systematic Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jul 22;61(8):1321. doi: 10.3390/medicina61081321. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40870366 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

