Dioscin alleviates the progression of osteoarthritis: an in vitro and in vivo study
- PMID: 37055831
- PMCID: PMC10100120
- DOI: 10.1186/s12950-023-00339-w
Dioscin alleviates the progression of osteoarthritis: an in vitro and in vivo study
Abstract
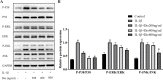
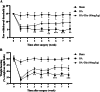
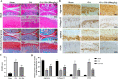
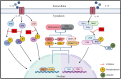
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common joint disease and is the main cause of physical disability in the elderly. Currently, there is no adequate therapeutic strategy to reverse the progression of OA. Many natural plant extracts have received attention in the treatment of OA due to their potential anti-inflammatory properties, and reduced incidence of adverse events. Dioscin (Dio), a natural steroid saponin, has been demonstrated to inhibit the release of inflammatory cytokines in mouse and rat models of various diseases, and has a protective effect in chronic inflammatory diseases. However, whether Dio alleviates OA progression remains to be explored. In this research, our purposes were to investigate the therapeutic potential of Dio in OA. The results demonstrated that Dio exerted anti-inflammatory effects by repressing NO, PGE2, iNOS and COX-2. Moreover, the application of Dio could repress IL-1β-induced overexpression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs, including MMP1, MMP3, and MMP13) and ADAMTS-5, and improve the synthesis of collagen II and aggrecan, which contribute to the maintenance of chondrocyte matrix homeostasis. The underlying mechanism involved the inhibition of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways by Dio. Furthermore, the treatment of Dio significantly improved the pain behaviors of rat OA models. The in vivo study revealed that Dio could ameliorate cartilage erosion and degradation. These results collectively indicate that Dio can be used as a promising and effective agent for the therapy of OA.
Keywords: Cartilage matrix; Chondrocyte; Dioscin; Inflammatory cytokines; Osteoarthritis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
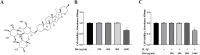




Similar articles
-
Schisandrin A Inhibits the IL-1β-Induced Inflammation and Cartilage Degradation via Suppression of MAPK and NF-κB Signal Pathways in Rat Chondrocytes.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 29;10:41. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00041. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30761007 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Erdosteine on interleukin-1β-stimulated inflammation via inhibiting the activation of MAPK, NF-κB, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in rat osteoarthritis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 15;873:172925. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.172925. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31958453
-
Enhancement of DUSP14 (dual specificity phosphatase 14) limits osteoarthritis progression by alleviating chondrocyte injury, inflammation and metabolic homeostasis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):7495-7507. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1979355. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34605731 Free PMC article.
-
Oroxin B alleviates osteoarthritis through anti-inflammation and inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancement of autophagy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 1;13:1060721. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1060721. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36531454 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cytokines in osteoarthritis pathophysiology.Biorheology. 2002;39(1-2):237-46. Biorheology. 2002. PMID: 12082286 Review.
Cited by
-
Scutellarein Ameliorated Chondrocyte Inflammation and Osteoarthritis in Rats.Curr Med Sci. 2024 Apr;44(2):355-368. doi: 10.1007/s11596-024-2854-6. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Curr Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38570439
-
Natural products for intervertebral disc degeneration: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 25;16:1605764. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1605764. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40786036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dioscin regulates oxidative stress and autophagy in uric acid-induced HK-2 cells through the P62-KEAP1-NRF2 signaling pathway.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 29;26(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04311-z. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40731269 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

