Mindfulness among lebanese university students and its indirect effect between mental health and wellbeing
- PMID: 37055857
- PMCID: PMC10100626
- DOI: 10.1186/s40359-023-01155-w
Mindfulness among lebanese university students and its indirect effect between mental health and wellbeing
Abstract
Background: University students are a high-risk population for developing mental health issues. Mindfulness, the non-judgmental awareness of the present moment, has an effective role in numerous psychological contexts among students. However, no previous studies have investigated the association between mindfulness, mental health and wellbeing among Lebanese university students. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the mediating effect of mindfulness in the association between mental health and wellbeing in this population.
Methods: This cross-sectional study enrolled 363 Lebanese university students recruited through convenience sampling (July-September 2021). The Wellbeing Index Scale, Lebanese Anxiety Scale, Patient Health Questionnaire and Freiburg Mindfulness Inventory were used to assess subjective well-being, anxiety, depression and mindfulness respectively.
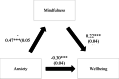
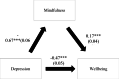
Results: Our findings showed that higher mindfulness (Beta = 0.18; p < 0.001) was significantly correlated with a higher wellbeing, whereas more depression (Beta=-0.36; p < 0.001) was significantly associated with a lower wellbeing. The results of the indirect effect analysis showed that mindfulness mediated the association between anxiety and wellbeing and between depression and wellbeing. Higher anxiety/depression were significantly associated with lower mindfulness and a lower wellbeing (direct effect). Moreover, higher mindfulness was significantly associated with a higher wellbeing.
Conclusion: Mindfulness is associated with improved wellbeing and plays an indirect role between mental health issues and wellbeing. Our results suggest that mindfulness presents an adaptive approach and coping method associated with improved students' wellbeing.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Lebanon; Mental health; Mindfulness; University students; Wellbeing.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Profiles of University Students in Terms of Sexual Dysfunction: The Role of Anxiety, Depression, Eating Attitudes, and Mindfulness.Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2024 May 30;26(3):23m03682. doi: 10.4088/PCC.23m03682. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2024. PMID: 38815268
-
Does self-esteem mediate the association between perfectionism and mindfulness among Lebanese university students?BMC Psychol. 2022 Nov 7;10(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s40359-022-00964-9. BMC Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36344999 Free PMC article.
-
Moderating Effect of Trait Mindfulness in the Association Between Problematic Social Media Use and Anxiety Among Lebanese University Students.Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2024 Apr 16;26(2):23m03664. doi: 10.4088/PCC.23m03664. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2024. PMID: 38684016
-
Effects of Mobile Mindfulness Meditation on the Mental Health of University Students: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Jan 3;25:e39128. doi: 10.2196/39128. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 36596239 Free PMC article.
-
Mindfulness to improve the mental health of university students. A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Public Health. 2023 Dec 4;11:1284632. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1284632. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38111480 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The mediating role of anxiety between child abuse and pain among a sample of Lebanese adults.Sci Rep. 2025 May 13;15(1):16559. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01689-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40360660 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the mediating role of emotional intelligence in the relationship between internet addiction and mental health among university students.PLOS Digit Health. 2024 Nov 20;3(11):e0000639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000639. eCollection 2024 Nov. PLOS Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39565763 Free PMC article.
-
A Multi- Mediation Analysis on the Impact of Social Media and Internet Addiction on University and High School Students' Mental Health Through Social Capital and Mindfulness.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Jan 2;22(1):57. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22010057. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39857510 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship among Internet Addiction, Moral Potency, Mindfulness, and Psychological Capital.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2024 Jun 16;14(6):1735-1756. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe14060115. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2024. PMID: 38921081 Free PMC article.
-
Healthy lifestyle promote Chinese university students' well-being: a cross-sectional network analysis.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 14;25(1):1770. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22894-y. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40369465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Briggs ARJ, Clark J, Hall I. Building bridges: understanding student transition to university. Qual High Educ. 2012 Apr;18(1):3–21.
-
- Macaskill A. The mental health of university students in the United Kingdom. Br J Guidance Couns. 2013 Aug;41(4):426–41.
-
- Bernier A, Larose S, Whipple N. Leaving home for college: a potentially stressful event for adolescents with preoccupied attachment patterns. Attach Hum Dev. 2005 Jun;7(2):171–85. - PubMed
-
- Auerbach RP, Mortier P, Bruffaerts R, Alonso J, Benjet C, Cuijpers P, Demyttenaere K, Ebert DD, Green JG, Hasking P, Murray E, Nock MK, Pinder-Amaker S, Sampson NA, Stein DJ, Vilagut G, Zaslavsky AM, Kessler RC, WHO WMH-ICS Collaborators. WHO World Mental Health Surveys International College Student Project. Prevalence and distribution of mental disorders. J Abnorm Psychol. 2018 Oct;127(7):623–38. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Mental health: strengthening our response [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2021 Nov 30]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-strengthe...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

