Postural influence on intracranial fluid dynamics: an overview
- PMID: 37055862
- PMCID: PMC10100470
- DOI: 10.1186/s40101-023-00323-6
Postural influence on intracranial fluid dynamics: an overview
Abstract
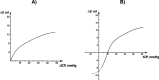
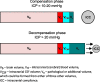
This review focuses on the effects of different body positions on intracranial fluid dynamics, including cerebral arterial and venous flow, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) hydrodynamics, and intracranial pressure (ICP). It also discusses research methods used to quantify these effects. Specifically, the implications of three types of body positions (orthostatic, supine, and antiorthostatic) on cerebral blood flow, venous outflow, and CSF circulation are explored, with a particular emphasis on cerebrovascular autoregulation during microgravity and head-down tilt (HDT), as well as posture-dependent changes in cerebral venous and CSF flow, ICP, and intracranial compliance (ICC). The review aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of intracranial fluid dynamics during different body positions, with the potential to enhance our understanding of intracranial and craniospinal physiology.
Keywords: Brain blood flow; Cerebral autoregulation; Cerebrospinal fluid; Craniospinal system; Head-down tilt; Head-up tilt; Intracranial compliance; Intracranial pressure; Postural changes.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wahl M, Schilling L. Regulation of cerebral blood flow–a brief review. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 1993;59:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Marshall-Goebel K, Ambarki K, Eklund A, et al. Effects of short-term exposure to head-down tilt on cerebral hemodynamics: a prospective evaluation of a spaceflight analog using phase-contrast MRI. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016;120(12):1466–1473. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00841.2015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

