Xeno-free cultured mesenchymal stromal cells release extracellular vesicles with a "therapeutic" miRNA cargo ameliorating cartilage inflammation in vitro
- PMID: 37056573
- PMCID: PMC10086204
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.77597
Xeno-free cultured mesenchymal stromal cells release extracellular vesicles with a "therapeutic" miRNA cargo ameliorating cartilage inflammation in vitro
Abstract
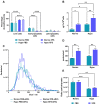
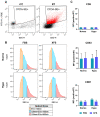
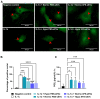
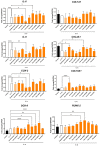
Rationale: Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs)-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) emerged as an innovative strategy for the treatment of chronic disorders such as osteoarthritis (OA). Biological activity of EVs is generally driven by their cargo, which might be influenced by microenvironment. Therefore, pre-conditioning strategies, including modifications in culture conditions or oxygen tension could directly impact on MSCs paracrine activity. In this study we selected an appropriate preconditioning system to induce cells to perform the most suitable therapeutic response by EV-encapsulated bioactive factors. Methods: A xeno-free supplement (XFS) was used for isolation and expansion of MSCs and compared to conventional fetal bovine serum (FBS) culture. Bone Marrow-derived MSCs (BMSCs) were pre-conditioned under normoxia (20% O2) or under hypoxia (1% O2) and EVs production was evaluated. Anti-OA activity was evaluated by using an in vitro inflammatory model. miRNA content was also explored, to select putative miRNA that could be involved in a biological function. Results: Modulation of IL-6, IL-8, COX-2 and PGE2 was evaluated on hACs simultaneously treated with IL-1α and BMSC-derived EVs. FBS-sEVs exerted a blunt inhibitory effect, while a strong anti-inflammatory outcome was achieved by XFS-sEVs. Interestingly, in both cases hypoxia pre-conditioning allowed to increase EVs effectiveness. Analysis of miRNA content showed the upregulation in XFS-hBMSC-derived EVs of miRNA known to have a chondroprotective role, such as let-7b-5p, miR-17, miR-145, miR-21-5p, miR-214-3p, miR-30b-5p, miR-30c-5p. Activated pathways and target genes were investigated in silico and upregulated miRNAs functionally validated in target cells. MiR-145 and miR-214 were found to protect chondrocytes from IL-1α-induced inflammation and to reduce production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Conclusions: XFS medium was found to be suitable for isolation and expansion of MSCs, secreting EVs with a therapeutic cargo. The application of cells cultured exclusively in XFS overcomes issues of safety associated with serum-containing media and makes ready-to-use clinical therapies more accessible.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; mesenchymal stromal cells; microRNA; osteoarthritis; xeno free medium.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Toh WS, Lai RC, Hui JHP, Lim SK. MSC exosome as a cell-free MSC therapy for cartilage regeneration: Implications for osteoarthritis treatment. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;67:56–64. - PubMed
-
- de Bari C, Roelofs AJ. Stem cell-based therapeutic strategies for cartilage defects and osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018;40:74–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

