The crucial role and mechanism of insulin resistance in metabolic disease
- PMID: 37056675
- PMCID: PMC10086443
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1149239
The crucial role and mechanism of insulin resistance in metabolic disease
Abstract
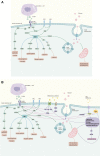
Insulin resistance (IR) plays a crucial role in the development and progression of metabolism-related diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, tumors, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and provides the basis for a common understanding of these chronic diseases. In this study, we provide a systematic review of the causes, mechanisms, and treatments of IR. The pathogenesis of IR depends on genetics, obesity, age, disease, and drug effects. Mechanistically, any factor leading to abnormalities in the insulin signaling pathway leads to the development of IR in the host, including insulin receptor abnormalities, disturbances in the internal environment (regarding inflammation, hypoxia, lipotoxicity, and immunity), metabolic function of the liver and organelles, and other abnormalities. The available therapeutic strategies for IR are mainly exercise and dietary habit improvement, and chemotherapy based on biguanides and glucagon-like peptide-1, and traditional Chinese medicine treatments (e.g., herbs and acupuncture) can also be helpful. Based on the current understanding of IR mechanisms, there are still some vacancies to follow up and consider, and there is also a need to define more precise biomarkers for different chronic diseases and lifestyle interventions, and to explore natural or synthetic drugs targeting IR treatment. This could enable the treatment of patients with multiple combined metabolic diseases, with the aim of treating the disease holistically to reduce healthcare expenditures and to improve the quality of life of patients to some extent.
Keywords: NAFLD; T2DM; insulin resistance; metabolic disease; obesity.
Copyright © 2023 Zhao, An, Yang, Sun, Ji and Lian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Preexisting Diabetes and Pregnancy: An Endocrine Society and European Society of Endocrinology Joint Clinical Practice Guideline.Eur J Endocrinol. 2025 Jun 30;193(1):G1-G48. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvaf116. Eur J Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40652450
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Single Herbal Medicine for Insulin Resistance: Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 Jun 10;14:e68915. doi: 10.2196/68915. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40493913 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In vitro digestion and fecal fermentation behaviors of exopolysaccharide from Morchella esculenta and its impacts on hypoglycemic activity via PI3K/Akt signaling and gut microbiota modulation.Food Chem X. 2024 Oct 2;24:101870. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101870. eCollection 2024 Dec 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 39431209 Free PMC article.
-
Celiac Disease, Gluten-Free Diet and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 25;16(13):2008. doi: 10.3390/nu16132008. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38999756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin Resistance in Long COVID-19 Syndrome.J Pers Med. 2024 Aug 28;14(9):911. doi: 10.3390/jpm14090911. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39338165 Free PMC article.
-
Association of remnant cholesterol with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: mediation analyses from NHANES 1999-2020.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Dec 18;23(1):404. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02393-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39695677 Free PMC article.
-
In-silico evaluation of diffractaic acid as novel anti-diabetic inhibitor against dipeptidyl peptidase IV enzyme.In Silico Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 10;13(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s40203-025-00321-9. eCollection 2025. In Silico Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39944121
References
-
- Muniyappa R, Madan R, Varghese RT. Assessing insulin sensitivity and resistance in humans. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, editors. Endotext. South Dartmouth (MA: MDText.com; Inc. Copyright © 2000-2021; MDText.com; Inc.; 2000. eng. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical