Crosstalk between omega-6 oxylipins and the enteric nervous system: Implications for gut disorders?
- PMID: 37056732
- PMCID: PMC10086145
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1083351
Crosstalk between omega-6 oxylipins and the enteric nervous system: Implications for gut disorders?
Abstract
The enteric nervous system (ENS) continues to dazzle scientists with its ability to integrate signals, from the outside as well as from the host, to accurately regulate digestive functions. Composed of neurons and enteric glial cells, the ENS interplays with numerous neighboring cells through the reception and/or the production of several types of mediators. In particular, ENS can produce and release n-6 oxylipins. These lipid mediators, derived from arachidonic acid, play a major role in inflammatory and allergic processes, but can also regulate immune and nervous system functions. As such, the study of these n-6 oxylipins on the digestive functions, their cross talk with the ENS and their implication in pathophysiological processes is in full expansion and will be discussed in this review.
Keywords: diet; enteric nervous system; inflammation; omega-3; omega-6.
Copyright © 2023 Mantel, Derkinderen, Bach-Ngohou, Neunlist and Rolli-Derkinderen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
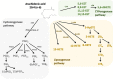
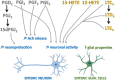
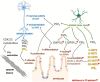
 ) are cells, oxylipins or cellular functions deficient in chronic inflammatory disease that is Crohn’s disease (CD).
) are cells, oxylipins or cellular functions deficient in chronic inflammatory disease that is Crohn’s disease (CD).References
-
- Ligumsky M, Karmeli F, Sharon P, Zor U, Cohen F, Rachmilewitz D. Enhanced thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin production by cultured rectal mucosa in ulcerative colitis and its inhibition by steroids and sulfasalazine. Gastroenterology. (1981) 81:444–9. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(81)90594-1, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

