miR-379-5p regulates the proliferation, cell cycle, and cisplatin resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting ROR1
- PMID: 37056860
- PMCID: PMC10086902
miR-379-5p regulates the proliferation, cell cycle, and cisplatin resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting ROR1
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the regulatory mechanism microRNA miR-379-5p in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
Methods: We collected serum samples from patients with OSCC and examined the expression of miR-379-5p and receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1) by real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blot. OSCC cells were purchased for molecular research, cell multiplication was tested using the BrdU assay, cell cycle was tested using flow cytometry, and resistance to cisplatin (DDP) was assessed using the MTT assay.
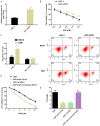
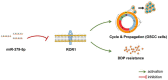
Results: miR-379-5p expression was downregulated and ROR1 expression was upregulated in the serum of OSCC patients, and the area under the curve for OSCC identified by miR-379-5p and ROR1 was not less than 0.800. In the cell function test, overexpression of miR-379-5p could suppress the proliferation, cell cycle, and DDP resistance of OSCC cells. miR-379-5p could negatively regulate ROR1. Inhibition of ROR1 expression had a similar effect after the re-expression of miR-379-5p. Co-overexpression of miR-379-5p and ROR1 counteracted the above inhibitory effects on the proliferation, cell cycle, and DDP resistance of OSCC cells.
Conclusion: miR-379-5p in OSCC regulates the proliferation, cell cycle, and DDP resistance of tumor cells by targeting ROR1.
Keywords: DDP resistance; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; ROR1; miR-379-5p.
AJTR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
