Reversing inflammatory microenvironment by a single intra-articular injection of multi-stimulus responsive lipogel to relieve rheumatoid arthritis and promote joint repair
- PMID: 37056918
- PMCID: PMC10085779
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100622
Reversing inflammatory microenvironment by a single intra-articular injection of multi-stimulus responsive lipogel to relieve rheumatoid arthritis and promote joint repair
Abstract
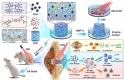
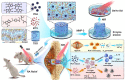
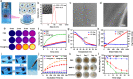
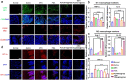
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common chronic disease dominated by inflammatory synovitis, which is characterized with hyperplastic synovium, up-regulated matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression, hypoxic joint cavity and excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation. Such local adverse microenvironment in RA joints further exacerbates the infiltration of synovial inflammatory cells, especially M1-type macrophages. Regulating intra-articular pathological conditions, eliminating excess M1 macrophages or converting them to an anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype may break the vicious progression circle. Herein, we develop a multi-stimulus responsive lipogel as effective platform to relieve RA symptoms and promote articular cartilage recovery via reversing its inflammatory microenvironment. The injectable lipogel is fabricated by loading polydopamine nanoparticles and methotrexate into a thermosensitive gel, and intra-articularly injected to form the therapeutic depot (PDA/MTX@TSG) in situ. The gel degrades slowly under esterase hydrolysis, and maintains sustained drug release in physiological conditions. Meanwhile, it can 1) induce a reversible gel-sol phase transition upon mild photothermal treatment (external NIR light control), and 2) specifically respond to MMP-rich RA microenvironment (internal enzymatic hydrolysis effect). Such stimulus-responsive system can deliver therapeutic components in a controllable manner, and significantly reverse adverse inflammatory microenvironment of RA joints through ROS eliminating, hypoxia alleviating, and M1-M2 macrophage polarization effects. Animal experiments indicate that observable RA relief and joint repair are realized after a single lipogel injection combined with NIR irradiation. Our study highlights the importance of altering local RA microenvironment via anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization, and therefore presents a potent therapeutic strategy for RA treatment in clinical intervention.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Lipogel; Macrophage polarization; Methotrexate; Reactive oxygen species; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Manganese Dioxide-Based pH-Responsive Multifunctional Nanoparticles Deliver Methotrexate for Targeted Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment.Biomater Res. 2025 May 14;29:0187. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0187. eCollection 2025. Biomater Res. 2025. PMID: 40371263 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Oxygen Generation and Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging by Manganese Ferrite/Ceria Co-decorated Nanoparticles for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment.ACS Nano. 2019 Mar 26;13(3):3206-3217. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b08785. Epub 2019 Mar 7. ACS Nano. 2019. PMID: 30830763
-
Prolonged, staged, and self-regulated methotrexate release coupled with ROS scavenging in an injectable hydrogel for rheumatoid arthritis therapy.J Control Release. 2024 Nov;375:60-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.08.046. Epub 2024 Sep 4. J Control Release. 2024. PMID: 39216600
-
Advanced application of stimuli-responsive drug delivery system for inflammatory arthritis treatment.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Feb 21;14:100223. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100223. eCollection 2022 Mar. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35243298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis.Front Immunol. 2022 May 19;13:867260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867260. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35663975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound-mediated nanomaterials for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 Mar;114:107270. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107270. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 39961217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polydopamine nanomaterials and their potential applications in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2289846. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2289846. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 38069584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCL7 promotes macrophage polarization and synovitis to exacerbate rheumatoid arthritis.iScience. 2025 Mar 7;28(4):112177. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112177. eCollection 2025 Apr 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40224025 Free PMC article.
-
Natural biomimetic nano-system for drug delivery in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a literature review of the last 5 years.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 May 9;11:1385123. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1385123. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38784236 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cavender D., Haskard D., Yu C.L., Iguchi T., Miossec P., Oppenheimer-Marks N., Ziff M. Pathways to chronic inflammation in rheumatoid synovitis, Fed. SAVE Proc. 1987;46(1):113–117. - PubMed
-
- Kim J., Kim H.Y., Song S.Y., Go S.H., Sohn H.S., Baik S., Soh M., Kim K., Kim D., Kim H.C., Lee N., Kim B.S., Hyeon T. Synergistic oxygen generation and reactive oxygen species scavenging by manganese ferrite/ceria Co-decorated nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. ACS Nano. 2019;13(3):3206–3217. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b08785. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Giannini D., Antonucci M., Petrelli F., Bilia S., Alunno A., Puxeddu I. One year in review 2020: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020;38(3):387–397. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

