Tectorigenin targets PKACα to promote GLUT4 expression in skeletal muscle and improve insulin resistance in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 37056927
- PMCID: PMC10086741
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.80125
Tectorigenin targets PKACα to promote GLUT4 expression in skeletal muscle and improve insulin resistance in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
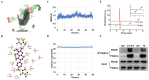
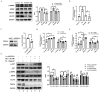
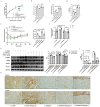
The decreased expression and dysfunction of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4), the insulin-responsive glucose transporter, are closely related to the occurrence of insulin resistance (IR). To improve the expression of GLUT4 may represent a promising strategy to prevent and treat IR and type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Here, we demonstrate that the natural compound tectorigenin (TG) enhances GLUT4 expression, glucose uptake and insulin responsiveness via activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) signaling in both normal and IR skeletal muscle cells and tissues. Accordingly, prophylactic and therapeutic uses of TG can significantly ameliorate IR and hyperglycemia in T2DM mice. Mechanistically, we identify protein kinase A catalytic subunit α (PKACα) as the target of TG to increase GLUT4 expression and TG-PKACα binding promotes the dissociation of PKACα from the regulatory subunits, leading to the activation of PKA/AMPK signaling. PKACα knockdown in local quadriceps muscles almost completely abolished the therapeutic effects of TG on IR and T2DM, as well as the enhancement on AMPK signaling and GLUT4 expression in skeletal muscle. This study supports TG as a new drug candidate to treat IR and its related diseases, but also enriches our knowledge of PKA signaling in glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle.
Keywords: AMPK; GLUT4; PKACα; insulin resistance; tectorigenin.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nature reviews Endocrinology. 2018;14:88–98. - PubMed
-
- Cheatham B. GLUT4 and company: SNAREing roles in insulin-regulated glucose uptake. Trends in endocrinology and metabolism: TEM. 2000;11:356–61. - PubMed
-
- Alam F, Islam MA, Khalil MI, Gan SH. Metabolic Control of Type 2 Diabetes by Targeting the GLUT4 Glucose Transporter: Intervention Approaches. Current pharmaceutical design. 2016;22:3034–49. - PubMed
-
- Zanquetta MM, Alves-Wagner AB, Mori RC, Campello RS, Machado UF. Recovery of insulin sensitivity and Slc2a4 mRNA expression depend on T3 hormone during refeeding. Metabolism: clinical and experimental. 2014;63:328–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

