From recurrent rhabdomyolysis in a young adult to carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency
- PMID: 37056952
- PMCID: PMC10088049
- DOI: 10.22551/2023.38.1001.10238
From recurrent rhabdomyolysis in a young adult to carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency
Abstract
Metabolic myopathies are a diverse group of rare genetic disorders associated with recurrent episodes of rhabdomyolysis, induced by triggers such as fever or exercise. In these disorders, the energetic metabolism is compromised resulting in damage of the muscle cells. The diagnosis can be challenging but is essential for the correct treatment. Carnitine palmitoytransferase II (CPT-II) deficiency is the most common long-chain fatty acid oxidation defect, with the adulthood form requiring additional external triggers. The authors present a case of a young-male adult with recurrent episodes of rhabdomyolysis, one of them presented with acute renal failure and acute hepatitis. The diagnostic is demanding, which requires a high level of suspicion. The adequate treatment of these patients improves the muscle function and prevents other episodes of severe rhabdomyolysis.
Keywords: CPT II deficiency; acute renal failure; hepatitis; rhabdomyolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work.No conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
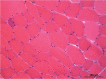
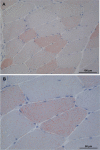

References
-
- Uzel B, Altiparmak MR, Ataman R, et al. Acute renal failure due to carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency. Neth J Med. 2003;61(12):417–420. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
