Post-myocardial infarction fibrosis: Pathophysiology, examination, and intervention
- PMID: 37056987
- PMCID: PMC10086160
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1070973
Post-myocardial infarction fibrosis: Pathophysiology, examination, and intervention
Abstract
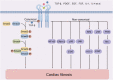
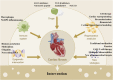
Cardiac fibrosis plays an indispensable role in cardiac tissue homeostasis and repair after myocardial infarction (MI). The cardiac fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation and extracellular matrix collagen deposition are the hallmarks of cardiac fibrosis, which are modulated by multiple signaling pathways and various types of cells in time-dependent manners. Our understanding of the development of cardiac fibrosis after MI has evolved in basic and clinical researches, and the regulation of fibrotic remodeling may facilitate novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, and finally improve outcomes. Here, we aim to elaborate pathophysiology, examination and intervention of cardiac fibrosis after MI.
Keywords: antifibrotic therapy; cardiac remodeling; extracellular matrix; fibroblast; fibrosis; myocardial infarction; myofibroblast.
Copyright © 2023 Yin, Yin, Pan, Zhang, Fan, Li, Zhai, Jiang, Hao, Wang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aboulgheit A., Karbasiafshar C., Zhang Z., Sabra M., Shi G., Tucker A., et al. (2021). Lactobacillus plantarum probiotic induces Nrf2-mediated antioxidant signaling and eNOS expression resulting in improvement of myocardial diastolic function. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 321, H839–h849. 10.1152/ajpheart.00278.2021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

