Caregiving burden, depression, and anxiety among family caregivers of patients with cancer: An investigation of patient and caregiver factors
- PMID: 37057172
- PMCID: PMC10086361
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1059605
Caregiving burden, depression, and anxiety among family caregivers of patients with cancer: An investigation of patient and caregiver factors
Abstract
Background: Caring for patients with cancer can result in significant burden, anxiety, and depression among family caregivers, leading to alterations in their mental and physical wellbeing. Evidence on the level of cancer caregivers' burden, depression, anxiety, their role in assisting their patients, and other patient and caregiver factors that play in improving/worsening the outcomes, is limited. This study explored the prevalence of caregiving burden, depression, and anxiety with a focus on the patient and caregiver-related factors among cancer family caregivers.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted on the population of caregivers of adult patients with cancer in Zanjan, Iran between 2019 and 2020. The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI), and the Zarit Burden Inventory (ZBI) were used to measure outcome variables. Clinical and basic characteristics of the caregivers and patients were also collected. An independent samples t-test, analysis of variance, Pearson's correlation coefficient, and stepwise linear regression were performed using SPSS software version 26.
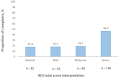
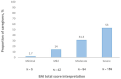
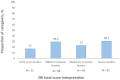
Results: Mean ± standard deviation age of the caregivers (167 men and 133 women) was 40.77 ± 12.56. Of the caregivers, 46.3, 53, and 30.7% showed severe depression, anxiety, and burden, respectively. There was a significant positive correlation between ZBI with both BDI [r (298) = 0.19, p < 0.01] and BAI [r (298) = 0.20, p < 0.01]. Caregiving ≥24 months (B = 14.36, p < 0.001), outpatient care setting (B = -12.90, p < 0.001), being retired (B = -12.90, p < 0.001), depression (B = 0.28, p < 0.001), supplemental health insurance (B = -7.79, p < 0.001), being illiterate (B = 7.77, p < 0.01), surgery (B = 8.55, p < 0.01), ECOG1 (B = 4.88, p < 0.01), and patient's age (B = 0.11, p < 0.05) were found to be significant predictors of caregiving burden.
Conclusion: High levels of depression, anxiety, and burden were observed among the caregivers of patients with cancer. These findings underline the importance of paying close attention to the needs and psychological challenges of this population.
Keywords: anxiety; burden; cancer patient; depression; family caregiver.
Copyright © 2023 Karimi Moghaddam, Rostami, Zeraatchi, Mohammadi Bytamar, Saed and Zenozian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caregiving burden, depression, and anxiety in family caregivers of patients with cancer.Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2021 Feb;50:101882. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2020.101882. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2021. PMID: 33421929
-
Burden and associated characteristics in caregivers of Parkinson's disease patients.Psychogeriatrics. 2024 Nov;24(6):1297-1304. doi: 10.1111/psyg.13191. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Psychogeriatrics. 2024. PMID: 39238200
-
Predictors of depression and anxiety among caregivers of hospitalised advanced cancer patients.Singapore Med J. 2018 Nov;59(11):572-577. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2018066. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Singapore Med J. 2018. PMID: 29876580 Free PMC article.
-
[Caregiver burden in relatives of persons with schizophrenia: an overview of measure instruments].Encephale. 2003 Mar-Apr;29(2):137-47. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 14567165 Review. French.
-
Caregivers' Burden in Patients With Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia and Its Relationship With Anxiety and Depression in Caregivers: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2023 Oct 22;15(10):e47497. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47497. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38022267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Moral conflicts among patients-caregivers dyads in oncological care pathway: a systematic review of the ethical literature.Support Care Cancer. 2025 Jun 6;33(7):548. doi: 10.1007/s00520-025-09548-w. Support Care Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40474016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Effects of the Mobile Health (mHealth) Psychoeducation and Benson Relaxation Technique in Reducing the Caregiving Burden of Cancer Patients in Bangladesh: A Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.Cureus. 2024 Mar 4;16(3):e55520. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55520. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38576646 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of caregiving burden on serum homocysteine and folate levels in spouses of patients with cognitive impairment.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025 Feb 24;9:25424823251322499. doi: 10.1177/25424823251322499. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025. PMID: 40034509 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the relations between psychosocial and caregiving factors with mental health among Vietnamese family caregivers of hospitalized lung cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 23;15(1):14078. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96409-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40269033 Free PMC article.
-
Patients' and caregivers' experiences of familial and social support in resource-poor settings: A systematically constructed review and meta-synthesis.Palliat Care Soc Pract. 2025 Jun 27;19:26323524251349840. doi: 10.1177/26323524251349840. eCollection 2025. Palliat Care Soc Pract. 2025. PMID: 40584974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbasi A., Shamsizadeh M., Asayesh H., Rahmani H., Hoseini S. A., Talebi M., et al. . (2013). The relationship between caregiver burden with coping strategies in family caregivers of cancer patients. IJPN 1, 62–71.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources