A systematic review and meta-analysis of the seroconversion rates and adverse effects of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine and COVID-19 viral vector vaccine in kidney transplant recipient patients
- PMID: 37057765
- PMCID: PMC10120468
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2196893
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the seroconversion rates and adverse effects of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine and COVID-19 viral vector vaccine in kidney transplant recipient patients
Abstract
Patients received kidney transplantation (KTR) have a low seroconversion rate after vaccination. Our objective was to compare the seroconversion rates and adverse effects of additional different vaccinations in KTR patients in existing studies. Databases such as PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, ClinicalTrials.gov and others. Three high-quality RCT were included and showed no statistical difference in seroconversion rates between the two vaccines (RR = 0.93[0.76,1.13]). There was no statistical difference in seroconversion rates between the sexes, for men (RR = 0.93[0.69,1.25]) and women (RR = 0.91[0.62,1.33]). Among the adverse effects there was no statistically significant difference in fever (RR = 1.06[0.44,2.57]), while for injection site pain there was a statistically significant difference (RR = 1.14[1.18,1.84]). There was no significant difference in seroconversion rates in patients with KTR who received the two additional vaccines. Patients injected with the viral vector vaccine were less painful than those injected with the mRNA vaccine.
Keywords: COVID-19; adverse effects; kidney transplant recipient; mRNA vaccine; seroconversion rate; viral vector vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


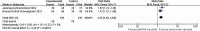
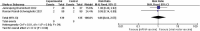
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
