A plasma membrane-associated glycolytic metabolon is functionally coupled to KATP channels in pancreatic α and β cells from humans and mice
- PMID: 37058408
- PMCID: PMC10513404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112394
A plasma membrane-associated glycolytic metabolon is functionally coupled to KATP channels in pancreatic α and β cells from humans and mice
Abstract
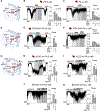
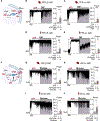
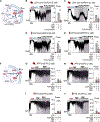
The ATP-sensitive K+ (KATP) channel is a key regulator of hormone secretion from pancreatic islet endocrine cells. Using direct measurements of KATP channel activity in pancreatic β cells and the lesser-studied α cells, from both humans and mice, we provide evidence that a glycolytic metabolon locally controls KATP channels on the plasma membrane. The two ATP-consuming enzymes of upper glycolysis, glucokinase and phosphofructokinase, generate ADP that activates KATP. Substrate channeling of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate through the enzymes of lower glycolysis fuels pyruvate kinase, which directly consumes the ADP made by phosphofructokinase to raise ATP/ADP and close the channel. We further show the presence of a plasma membrane-associated NAD+/NADH cycle whereby lactate dehydrogenase is functionally coupled to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. These studies provide direct electrophysiological evidence of a KATP-controlling glycolytic signaling complex and demonstrate its relevance to islet glucose sensing and excitability.
Keywords: CP: Metabolism; K(ATP) channel; glycolysis; glycolytic metabolon; inside-out excised patch clamp; metabolic compartmentation; pyruvate kinase.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

