NP and 9311 are excellent population parents for screening QTLs of potassium-efficient rice
- PMID: 37058514
- PMCID: PMC10104323
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284510
NP and 9311 are excellent population parents for screening QTLs of potassium-efficient rice
Abstract
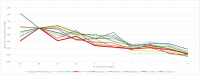
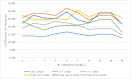
High and stable rice yields are critical to global food security, and potassium-deficient soils in East Asia have seriously limited rice production in the regions. It is feasible to screen potassium efficient quantitative trait locus(QTLs) from existing rice varieties to cope with rice production in potassium-deficient areas, and the selection of population parents is the key to locating major QTLs. After a long period of natural selection, potassium efficient rice varieties mainly exist in the region where the soil potassium level is low. The present study chose the representative twelve high-yielding rice varieties in east Asia, firstly, to measure plant height, fresh sheath weight, and fresh blade weight under hydroponic conditions. Based on the difference and consistency of the three parameters, NP as low potassium tolerant, and 9311 as low potassium sensitive rice variety were screened. We further analyzed the relative values of the six parameters of NP and 9311 treated with a culture medium containing different potassium (K+) concentrations and showed that the two varieties significantly differed in multiple low potassium concentrations. Meanwhile, we calculated the coefficient of variation of twelve rice varieties and most of those parameters reached a maximum at 4 mg/L K+, indicating that this concentration was suitable for screening potassium-efficient rice. We also measured the potassium content and the potassium-related traits in NP and 9311 tissues, and found that NP and 9311 significantly differed in potassium translocation. These differences may be responsible for the long-distance transport of potassium from the root to the aboveground part. In conclusion, we identified a pair of parents with significant differences in potassium translocation, which can be used to locate the relevant QTLs with high potassium efficiency to cope with the crisis of soil potassium deficiency in East Asia.
Copyright: © 2023 Liu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of Quantitative Trait Loci Associated with Nutrient Use Efficiency Traits, Using SNP Markers in an Early Backcross Population of Rice (Oryza sativa L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 19;20(4):900. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040900. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30791412 Free PMC article.
-
QTL analysis of novel genomic regions associated with yield and yield related traits in new plant type based recombinant inbred lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Aug 9;12:137. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-137. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 22876968 Free PMC article.
-
From QTL to variety-harnessing the benefits of QTLs for drought, flood and salt tolerance in mega rice varieties of India through a multi-institutional network.Plant Sci. 2016 Jan;242:278-287. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 26566845
-
Genetic analysis of rice seedling traits related to machine transplanting under different seeding densities.BMC Genet. 2020 Nov 26;21(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12863-020-00952-1. BMC Genet. 2020. PMID: 33243137 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping QTLs for Salt Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) by Bulked Segregant Analysis of Recombinant Inbred Lines Using 50K SNP Chip.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 14;11(4):e0153610. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153610. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27077373 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The transcription factor OsNAC25 regulates potassium homeostasis in rice.Plant Biotechnol J. 2025 Mar;23(3):930-945. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14550. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Plant Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 39693105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heffer P, Prudhomme M, Tiejun RU. 2016–2020 fertilizer outlook (summary report). Phosphate & Compound Fertilizer. 2016.
-
- Santa-Mariea G, F R, J D. The HAK1 and HAK2 genes of barley encode high-affinity K + transporters that are also present in Arabidopsis. Plant Nutrition—Molecular Biology and Genetics. 1999:137–43. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-2685-6_18 - DOI
-
- Lin-sheng A, Jin-Shan N, Gong-fu L. Physiological Characterestics of K-Deficit Tolerent Rice Variety. Plant Physiology Communication. 1995;31(4):257–9.
-
- Guodong L, Gengling L. A NEW STRATEGY ALLEVIATING SHORTAGE OF POTASSIUM RESOURCE IN CHINA. Scientia Agricultura Sinica. 1995;28(1):25–32. https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:ZNYK.0.1995-01-003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

