Characterization of altered molecular mechanisms in Parkinson's disease through cell type-resolved multiomics analyses
- PMID: 37058563
- PMCID: PMC10104466
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo2467
Characterization of altered molecular mechanisms in Parkinson's disease through cell type-resolved multiomics analyses
Abstract
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. However, cell type-dependent transcriptional regulatory programs responsible for PD pathogenesis remain elusive. Here, we establish transcriptomic and epigenomic landscapes of the substantia nigra by profiling 113,207 nuclei obtained from healthy controls and patients with PD. Our multiomics data integration provides cell type annotation of 128,724 cis-regulatory elements (cREs) and uncovers cell type-specific dysregulations in cREs with a strong transcriptional influence on genes implicated in PD. The establishment of high-resolution three-dimensional chromatin contact maps identifies 656 target genes of dysregulated cREs and genetic risk loci, uncovering both potential and known PD risk genes. Notably, these candidate genes exhibit modular gene expression patterns with unique molecular signatures in distinct cell types, highlighting altered molecular mechanisms in dopaminergic neurons and glial cells including oligodendrocytes and microglia. Together, our single-cell transcriptome and epigenome reveal cell type-specific disruption in transcriptional regulations related to PD.
Figures





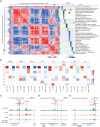
References
-
- J. Jankovic, Parkinson’s disease: Clinical features and diagnosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79, 368–376 (2008). - PubMed
-
- A. B. Singleton, M. Farrer, J. Johnson, A. Singleton, S. Hague, J. Kachergus, M. Hulihan, T. Peuralinna, A. Dutra, R. Nussbaum, S. Lincoln, A. Crawley, M. Hanson, D. Maraganore, C. Adler, M. R. Cookson, M. Muenter, M. Baptista, D. Miller, J. Blancato, J. Hardy, K. Gwinn-Hardy, α-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302, 841 (2003). - PubMed
-
- V. Bonifati, P. Rizzu, M. J. van Baren, O. Schaap, G. J. Breedveld, E. Krieger, M. C. Dekker, F. Squitieri, P. Ibanez, M. Joosse, J. W. van Dongen, N. Vanacore, J. C. van Swieten, A. Brice, G. Meco, C. M. van Duijn, B. A. Oostra, P. Heutink, Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299, 256–259 (2003). - PubMed
-
- D. Chang, M. A. Nalls, I. B. Hallgrimsdottir, J. Hunkapiller, M. van der Brug, F. Cai; International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium; 23andMe Research Team, G. A. Kerchner, G. Ayalon, B. Bingol, M. Sheng, D. Hinds, T. W. Behrens, A. B. Singleton, T. R. Bhangale, R. R. Graham, A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies 17 new Parkinson’s disease risk loci. Nat. Genet. 49, 1511–1516 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
-
- M. A. Nalls, N. Pankratz, C. M. Lill, C. B. Do, D. G. Hernandez, M. Saad, A. L. DeStefano, E. Kara, J. Bras, M. Sharma, C. Schulte, M. F. Keller, S. Arepalli, C. Letson, C. Edsall, H. Stefansson, X. Liu, H. Pliner, J. H. Lee, R. Cheng; International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC); Parkinson’s Study Group (PSG) Parkinson’s Research: The Organized GENetics Initiative (PROGENI); 23andMe; GenePD; NeuroGenetics Research Consortium (NGRC); Hussman Institute of Human Genomics (HIHG); Ashkenazi Jewish Dataset Investigator; Cohorts for Health and Aging Research in Genetic Epidemiology (CHARGE); North American Brain Expression Consortium (NABEC); United Kingdom Brain Expression Consortium (UKBEC); Greek Parkinson’s Disease Consortium; Alzheimer Genetic Analysis Group, M. A. Ikram, J. P. Ioannidis, G. M. Hadjigeorgiou, J. C. Bis, M. Martinez, J. S. Perlmutter, A. Goate, K. Marder, B. Fiske, M. Sutherland, G. Xiromerisiou, R. H. Myers, L. N. Clark, K. Stefansson, J. A. Hardy, P. Heutink, H. Chen, N. W. Wood, H. Houlden, H. Payami, A. Brice, W. K. Scott, T. Gasser, L. Bertram, N. Eriksson, T. Foroud, A. B. Singleton, Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 46, 989–993 (2014). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

