Offshore Wind Energy and Marine Biodiversity in the North Sea: Life Cycle Impact Assessment for Benthic Communities
- PMID: 37058594
- PMCID: PMC10134491
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.2c07797
Offshore Wind Energy and Marine Biodiversity in the North Sea: Life Cycle Impact Assessment for Benthic Communities
Abstract
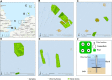
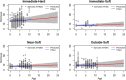
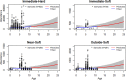
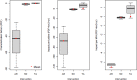
Large-scale offshore wind energy developments represent a major player in the energy transition but are likely to have (negative or positive) impacts on marine biodiversity. Wind turbine foundations and sour protection often replace soft sediment with hard substrates, creating artificial reefs for sessile dwellers. Offshore wind farm (OWF) furthermore leads to a decrease in (and even a cessation of) bottom trawling, as this activity is prohibited in many OWFs. The long-term cumulative impacts of these changes on marine biodiversity remain largely unknown. This study integrates such impacts into characterization factors for life cycle assessment based on the North Sea and illustrates its application. Our results suggest that there are no net adverse impacts during OWF operation on benthic communities inhabiting the original sand bottom within OWFs. Artificial reefs could lead to a doubling of species richness and a two-order-of-magnitude increase of species abundance. Seabed occupation will also incur in minor biodiversity losses in the soft sediment. Our results were not conclusive concerning the trawling avoidance benefits. The developed characterization factors quantifying biodiversity-related impacts from OWF operation provide a stepping stone toward a better representation of biodiversity in life cycle assessment.
Keywords: artificial reef; characterization factors; marine ecosystems; offshore wind farms; seabed occupation; species abundance; species richness; trawling avoidance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential marine benthic colonisers of offshore wind farms in the English channel: A functional trait-based approach.Mar Environ Res. 2023 Sep;190:106061. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2023.106061. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Mar Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37421705
-
Generalized changes of benthic communities after construction of wind farms in the southern North Sea.J Environ Manage. 2022 Aug 1;315:115173. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115173. Epub 2022 May 5. J Environ Manage. 2022. PMID: 35526396
-
Potential Impacts of Offshore Wind Farms on North Sea Stratification.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 11;11(8):e0160830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160830. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27513754 Free PMC article.
-
Ecological impacts of the expansion of offshore wind farms on trophic level species of marine food chain.J Environ Sci (China). 2024 May;139:226-244. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.05.002. Epub 2023 May 18. J Environ Sci (China). 2024. PMID: 38105050 Review.
-
Chemical emissions from offshore wind farms: From identification to challenges in impact assessment and regulation.Mar Pollut Bull. 2025 Jun;215:117915. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2025.117915. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Mar Pollut Bull. 2025. PMID: 40187202 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimal Environmental Siting of Future Wind Turbines in the North Sea.Environ Sci Technol. 2024 Dec 31;58(52):22944-22952. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.4c03861. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Environ Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39698735 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental implications of future offshore renewable energy development in Aotearoa New Zealand.J R Soc N Z. 2024 Oct 24;55(4):912-945. doi: 10.1080/03036758.2024.2406829. eCollection 2025. J R Soc N Z. 2024. PMID: 40337496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Climate-Smart Siting for renewable energy expansion.iScience. 2024 Aug 3;27(10):110666. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110666. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39351196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial niche differentiation and key driving factors of dominant benthic macroinvertebrates in Qinhuangdao City, China.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 5;15(1):24072. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09965-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40617884 Free PMC article.
-
Biodiversity Information of benthic Species at ARtificial structures - BISAR.Sci Data. 2025 Apr 10;12(1):604. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04920-1. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40210637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IEA . Offshore Wind Outlook 2019 IEA: Paris, 2019. https://www.iea.org/reports/offshore-wind-outlook-2019, License: CC BY 4.0 (accessed November 2019).
-
- Energinet; Gasunie; TenneT . Towards the First Hub-and-Spoke Project, 2021, p 59.
-
- Leopold M. F.; Camphuysen C. J.; Verdaat H.; Dijkman E. M.; Aarts G. M.; Poot M.; Fijn R.; Waardenburg B.. IMARES Wageningen UR. 1976, pp 1–269.
-
- Normandeau Associates, Inc. . Effects of Noise on Fish, Fisheries, and Invertebrates in the U.S. Atlantic and Arctic from Energy Industry Sound-Generating Activities, Workshop Report 2012, p 80.
-
- Lovich J. E.; Ennen J. R. Assessing the State of Knowledge of Utility-Scale Wind Energy Development and Operation on Non-Volant Terrestrial and Marine Wildlife. Appl. Energy 2013, 103, 52–60. 10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.10.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

