Th-1, Th-2, Th-9, Th-17, Th-22 type cytokine concentrations of critical COVID-19 patients after treatment with Remdesivir
- PMID: 37058846
- PMCID: PMC10036294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imbio.2023.152378
Th-1, Th-2, Th-9, Th-17, Th-22 type cytokine concentrations of critical COVID-19 patients after treatment with Remdesivir
Abstract
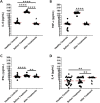
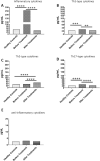
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) rapidly spread around the world causing a pandemic known as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Cytokine storm was directly correlated with severity of COVID-19 syndromes. We evaluated the levels of 13 cytokines in ICU hospitalized COVID-19 patients (n = 29) before, and after treatment with Remdesivir as well as in healthy controls (n = 29). Blood samples were obtained from ICU patients during ICU admission (before treatment) and 5 days after treatment with Remdesivir. A group of 29 age- and gender-matched healthy controls was also studied. Cytokine levels were evaluated by multiplex immunoassay method using a fluorescence labeled cytokine panel. In comparison to cytokine levels measured at ICU admission, serum levels were reduced of IL-6 (134.75 pg/mL vs. 20.73 pg/mL, P < 0.0001), TNF-α (121.67 pg/mL vs. 10.15 pg/mL, P < 0.0001) and IFN-γ (29.69 pg/mL vs. 22.27 pg/mL, P = 0.005), whereas serum level was increased of IL-4 (8.47 pg/mL vs. 12.44 pg/mL, P = 0.002) within 5 days after Remdesivir treatment. Comparing with before treatment, Remdesivir significantly reduced the levels of inflammatory (258.98 pg/mL vs. 37.43 pg/mL, P < 0.0001), Th1-type (31.24 pg/mL vs. 24.46 pg/mL, P = 0.007), and Th17-type (36.79 pg/mL vs. 26.22 pg/mL, P < 0.0001) cytokines in critical COVID-19 patients. However, after Remdesivir treatment, the concentrations of Th2-type cytokines were significantly higher than before treatment (52.69 pg/mL vs. 37.09 pg/mL, P < 0.0001). In conclusion, Remdesivir led to decrease levels of Th1-type and Th17-type cytokines and increase Th2-type cytokines in critical COVID-19 patients 5 days after treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; Critical COVID-19 patients; Cytokines storm; Inflammatory cytokines; Remdesivir treatment; SARS-CoV-2; Th1-type cytokines; Th17-type cytokines; Th2-type cytokines.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

