A molecular assessment of the practical potential of DNA-based computation
- PMID: 37058876
- PMCID: PMC10229437
- DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2023.102940
A molecular assessment of the practical potential of DNA-based computation
Abstract
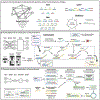
The immense information density of DNA and its potential for massively parallelized computations, paired with rapidly expanding data production and storage needs, have fueled a renewed interest in DNA-based computation. Since the construction of the first DNA computing systems in the 1990s, the field has grown to encompass a diverse array of configurations. Simple enzymatic and hybridization reactions to solve small combinatorial problems transitioned to synthetic circuits mimicking gene regulatory networks and DNA-only logic circuits based on strand displacement cascades. These have formed the foundations of neural networks and diagnostic tools that aim to bring molecular computation to practical scales and applications. Considering these great leaps in system complexity as well as in the tools and technologies enabling them, a reassessment of the potential of such DNA computing systems is warranted.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
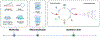
References
-
- IEA: Data Centres and Data Transmission Networks. IEA, Paris: 2020. Accessed 21/11/2022.
-
- Adleman LM: Molecular Computation of Solutions to Combinatorial Problems. Science (1979) 1994, 266:1021–1024. - PubMed
-
- Mao C, LaBean TH, Reif JH, Seeman NC: Logical computation using algorithmic self-assembly of DNA triple-crossover molecules. Nature 2000, 407:493–496. - PubMed
-
- Woods D, Doty D, Myhrvold C, Hui J, Zhou F, Yin P, Winfree E: Diverse and robust molecular algorithms using reprogrammable DNA self-assembly. Nature 2019, 567:366–372. - PubMed
-
This study constructed a set of DNA tiles comprised of 355 single DNA strands and performed numerous algorithms based upon the reprogrammable self-assembly of these tiles.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

