Pancreatic cancer: Advances and challenges
- PMID: 37059070
- PMCID: PMC10182830
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.02.014
Pancreatic cancer: Advances and challenges
Abstract
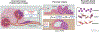
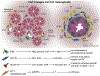
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the deadliest cancers. Significant efforts have largely defined major genetic factors driving PDAC pathogenesis and progression. Pancreatic tumors are characterized by a complex microenvironment that orchestrates metabolic alterations and supports a milieu of interactions among various cell types within this niche. In this review, we highlight the foundational studies that have driven our understanding of these processes. We further discuss the recent technological advances that continue to expand our understanding of PDAC complexity. We posit that the clinical translation of these research endeavors will enhance the currently dismal survival rate of this recalcitrant disease.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.A.L. has received consulting fees from Astellas Pharmaceuticals, Odyssey Therapeutics, and T-Knife Therapeutics, and is an inventor on patents pertaining to Kras-regulated metabolic pathways, redox control pathways in pancreatic cancer, and targeting the GOT1-pathway as a therapeutic approach (US patent no.: 2015126580-A1, 05/07/2015; US patent no.: 20190136238, 05/09/2019; International patent no.: WO2013177426-A2, 04/23/2015). A.M. receives royalties for a pancreatic cancer biomarker test from Cosmos Wisdom Biotechnology, and this financial relationship is managed and monitored by the UTMDACC Conflict of Interest Committee. A.M. is also listed as an inventor on a patent that has been licensed by Johns Hopkins University to ThriveEarlier Detection. A.M. serves as a consultant for Freenome and Tezcat Biotechnology.
Figures
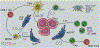
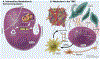
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 CA200468/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA274371/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA248160/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA260752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244931/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA220236/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA062203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA237421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA274274/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA264843/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA221707/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA241357/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA274154/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA271510/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

