The evolving landscape of PCSK9 inhibition in cancer
- PMID: 37059376
- PMCID: PMC10229316
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175721
The evolving landscape of PCSK9 inhibition in cancer
Abstract
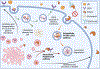
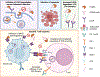
Cancer is a disease with a significant global burden in terms of premature mortality, loss of productivity, healthcare expenditures, and impact on mental health. Recent decades have seen numerous advances in cancer research and treatment options. Recently, a new role of cholesterol-lowering PCSK9 inhibitor therapy has come to light in the context of cancer. PCSK9 is an enzyme that induces the degradation of low-density lipoprotein receptors (LDLRs), which are responsible for clearing cholesterol from the serum. Thus, PCSK9 inhibition is currently used to treat hypercholesterolemia, as it can upregulate LDLRs and enable cholesterol reduction through these receptors. The cholesterol-lowering effects of PCSK9 inhibitors have been suggested as a potential mechanism to combat cancer, as cancer cells have been found to increasingly rely on cholesterol for their growth needs. Additionally, PCSK9 inhibition has demonstrated the potential to induce cancer cell apoptosis through several pathways, increase the efficacy of a class of existing anticancer therapies, and boost the host immune response to cancer. A role in managing cancer- or cancer treatment-related development of dyslipidemia and life-threatening sepsis has also been suggested. This review examines the current evidence regarding the effects of PCSK9 inhibition in the context of different cancers and cancer-associated complications.
Keywords: Cancer; Cholesterol; Hypercholesterolemia; Immune response; LDL; PCSK9.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New LDL-cholesterol lowering therapies: pharmacology, clinical trials, and relevance to acute coronary syndromes.Clin Ther. 2013 Aug;35(8):1082-98. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.06.019. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Clin Ther. 2013. PMID: 23932550 Review.
-
Targeting PCSK9 as a promising new mechanism for lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Aug;164:183-94. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.04.011. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27133571 Review.
-
The next generation of novel low-density lipoprotein cholesterol-lowering agents: proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 inhibitors.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Jul;73:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23578522 Review.
-
Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin Type 9 Inhibition for Autosomal Recessive Hypercholesterolemia-Brief Report.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Aug;36(8):1647-50. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307493. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27079874
-
PCSK9 Inhibition: Discovery, Current Evidence, and Potential Effects on LDL-C and Lp(a).Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2015 Jun;29(3):295-308. doi: 10.1007/s10557-015-6588-3. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2015. PMID: 26068408 Review.
Cited by
-
PCSK9 expression and cancer survival: a prognostic biomarker at the intersection of oncology and geroscience.Geroscience. 2025 Jun 27. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01733-3. Online ahead of print. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 40576911
-
Why make it if you can take it: review on extracellular cholesterol uptake and its importance in breast and ovarian cancers.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 6;43(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03172-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39243069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Causal Relationship between PCSK9 Inhibitors and Malignant Tumors: A Mendelian Randomization Study Based on Drug Targeting.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 21;15(1):132. doi: 10.3390/genes15010132. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275613 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer: A Dangerous Liaison.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025 Mar;45(3):359-371. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.319863. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025. PMID: 39781742 Review.
-
Targeting PCSK9, through an innovative cVLP-based vaccine, enhanced the therapeutic activity of a cVLP-HER2 vaccine in a preclinical model of HER2-positive mammary carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2025 Jan 30;23(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06126-w. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39885551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelwahed KS, Siddique AB, Mohyeldin MM, Qusa MH, Goda AA, Singh SS, Ayoub NM, King JA, Jois SD, El Sayed KA, 2020. Pseurotin A as a novel suppressor of hormone dependent breast cancer progression and recurrence by inhibiting PCSK9 secretion and interaction with LDL receptor. Pharmacological Research 158, 104847. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abifadel M, Varret M, Rabès J-P, Allard D, Ouguerram K, Devillers M, Cruaud C, Benjannet S, Wickham L, Erlich D, Derré A, Villéger L, Farnier M, Beucler I, Bruckert E, Chambaz J, Chanu B, Lecerf J-M, Luc G, Moulin P, Weissenbach J, Prat A, Krempf M, Junien C, Seidah NG, Boileau C, 2003. Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nature Genetics 34, 154–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

