Over-production of exopolysaccharide by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-3690 strain cutbacks its beneficial effect on the host
- PMID: 37059733
- PMCID: PMC10104810
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-32116-3
Over-production of exopolysaccharide by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-3690 strain cutbacks its beneficial effect on the host
Abstract
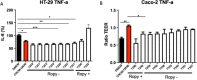
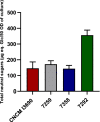
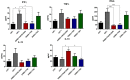
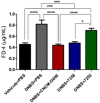
Most lactobacilli produce extracellular polysaccharides that are considered to contribute to the probiotic effect of many strains. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-3690 is an anti-inflammatory strain able to counterbalance gut barrier dysfunction. In this study ten spontaneous variants of CNCM I-3690 with different EPS-production were generated and characterized by their ropy phenotype, the quantification of the secreted EPS and genetic analysis. Amongst them, two were further analysed in vitro and in vivo: an EPS over-producer (7292) and a low-producer derivative of 7292 (7358, with similar EPS levels than the wild type (WT) strain). Our results showed that 7292 does not have anti-inflammatory profile in vitro, and lost the capacity to adhere to the colonic epithelial cells as well as the protective effect on the permeability. Finally, 7292 lost the protective effects of the WT strain in a murine model of gut dysfunction. Notably, strain 7292 was unable to stimulate goblet cell mucus production and colonic IL-10 production, all key features for the beneficial effect of the WT strain. Furthermore, transcriptome analysis of colonic samples from 7292-treated mice showed a down-regulation of anti-inflammatory genes. Altogether, our results point out that the increase of EPS production in CNCM I-3690 impairs its protective effects and highlight the importance of the correct EPS synthesis for the beneficial effects of this strain.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.D., T.S are employees of Danone Nutricia Research. The funder was involved in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data and in the writing of the manuscript. The rest of authors do not have conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Zheng, J. et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. (2020). - PubMed
-
- De Valdez GF, Torino MI, De Vuyst L, Mozzi F. Food grade heteropolysaccharides. On going research and future trends on biopolymers from lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Biotechnol. Food Sci. Policy. 2003;1:223–233.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

