Post-revascularization Ejection Fraction Prediction for Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Based on Myocardial Perfusion SPECT Imaging Radiomics: a Preliminary Machine Learning Study
- PMID: 37059890
- PMCID: PMC10407007
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-023-00820-1
Post-revascularization Ejection Fraction Prediction for Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Based on Myocardial Perfusion SPECT Imaging Radiomics: a Preliminary Machine Learning Study
Abstract
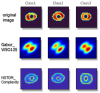
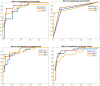
In this study, the ability of radiomics features extracted from myocardial perfusion imaging with SPECT (MPI-SPECT) was investigated for the prediction of ejection fraction (EF) post-percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) treatment. A total of 52 patients who had undergone pre-PCI MPI-SPECT were enrolled in this study. After normalization of the images, features were extracted from the left ventricle, initially automatically segmented by k-means and active contour methods, and finally edited and approved by an expert radiologist. More than 1700 2D and 3D radiomics features were extracted from each patient's scan. A cross-combination of three feature selections and seven classifier methods was implemented. Three classes of no or dis-improvement (class 1), improved EF from 0 to 5% (class 2), and improved EF over 5% (class 3) were predicted by using tenfold cross-validation. Lastly, the models were evaluated based on accuracy, AUC, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and F-score. Neighborhood component analysis (NCA) selected the most predictive feature signatures, including Gabor, first-order, and NGTDM features. Among the classifiers, the best performance was achieved by the fine KNN classifier, which yielded mean accuracy, AUC, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and F-score of 0.84, 0.83, 0.75, 0.87, 0.78, and 0.76, respectively, in 100 iterations of classification, within the 52 patients with 10-fold cross-validation. The MPI-SPECT-based radiomic features are well suited for predicting post-revascularization EF and therefore provide a helpful approach for deciding on the most appropriate treatment.
Keywords: Ejection fraction; Machine learning; Myocardial perfusion imaging; PCI; Quantitative features; Radiomics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Machine learning-based diagnosis and risk classification of coronary artery disease using myocardial perfusion imaging SPECT: A radiomics study.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 10;13(1):14920. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42142-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37691039 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial perfusion SPECT radiomic features reproducibility assessment: Impact of image reconstruction and harmonization.Med Phys. 2025 Feb;52(2):965-977. doi: 10.1002/mp.17490. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 39470363 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial Perfusion SPECT Imaging Radiomic Features and Machine Learning Algorithms for Cardiac Contractile Pattern Recognition.J Digit Imaging. 2023 Apr;36(2):497-509. doi: 10.1007/s10278-022-00705-9. Epub 2022 Nov 14. J Digit Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36376780 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Performance of PET Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Compared to SPECT in the Evaluation of Suspected CAD.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023 Apr;25(4):281-293. doi: 10.1007/s11886-023-01851-4. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36826689 Review.
-
[Role of perfusion myocardial scintigraphy with gated SPECT technique in the diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of patients with chronic coronary disease].Ital Heart J Suppl. 2002 Mar;3(3):309-18. Ital Heart J Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12040846 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
ELTIRADS framework for thyroid nodule classification integrating elastography, TIRADS, and radiomics with interpretable machine learning.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 13;15(1):8763. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93226-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40082527 Free PMC article.
-
Left Ventricular Myocardial Dysfunction Evaluation in Thalassemia Patients Using Echocardiographic Radiomic Features and Machine Learning Algorithms.J Digit Imaging. 2023 Dec;36(6):2494-2506. doi: 10.1007/s10278-023-00891-0. Epub 2023 Sep 21. J Digit Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37735309 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of model feature importance statistics to identify covariates that contribute most to model accuracy in prediction of insomnia.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 2;19(7):e0306359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306359. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38954735 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Cardiovascular Imaging and Interventional Cardiology: Emerging Trends and Clinical Implications.J Soc Cardiovasc Angiogr Interv. 2025 Mar 18;4(3Part B):102558. doi: 10.1016/j.jscai.2024.102558. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Soc Cardiovasc Angiogr Interv. 2025. PMID: 40230671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine Learning Applications in Acute Coronary Syndrome: Diagnosis, Outcomes and Management.Adv Ther. 2025 Feb;42(2):636-665. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-03060-z. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 39641854 Review.
References
-
- Authors Task Force, m, , et al. ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: The Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI) Eur Heart J. 2014;35(2541–2619):2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

