Neuregulin4 Acts on Hypothalamic ErBb4 to Excite Oxytocin Neurons and Preserve Metabolic Homeostasis
- PMID: 37060105
- PMCID: PMC10238187
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202204824
Neuregulin4 Acts on Hypothalamic ErBb4 to Excite Oxytocin Neurons and Preserve Metabolic Homeostasis
Abstract
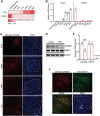
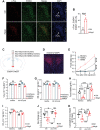
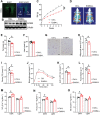
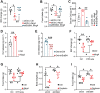
Neuregulin 4 (Nrg4) is an adipose tissue-enriched secreted factor that modulates glucose and lipid metabolism. Nrg4 is closely associated with obesity and preserves diet-induced metabolic disorders. However, the specific mechanisms via which Nrg4 regulates metabolic homeostasis remain incompletely understood. Here, this work finds that the Nrg4 receptor, ErbB4, is highly expressed in the hypothalamus, and the phosphorylation of hypothalamic ErbB4 is reduced in diet-induced obesity (DIO) mice. Peripheral Nrg4 can act on ErbB4 via blood circulation and excite neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus (PVN). Central administration of recombinant Nrg4 protein (rNrg4) reduces obesity and related metabolic disorders by influencing energy expenditure and intake. Overexpression of ErbB4 in the PVN protects against obesity, whereas its knock down in oxytocin (Oxt) neuron accelerates obesity. Furthermore, Nrg4-ErbB4 signaling excites Oxt release, and ablation of Oxt neuron considerably attenuates the effect of Nrg4 on energy balance. These data suggest that the hypothalamus is a key target of Nrg4, which partially explains the multifaceted roles of Nrg4 in metabolism.
Keywords: ErbB4; hypothalamus; neuregulin4; obesity; oxytocin neuron.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Energy Expenditure Homeostasis Requires ErbB4, an Obesity Risk Gene, in the Paraventricular Nucleus.eNeuro. 2023 Sep 25;10(9):ENEURO.0139-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0139-23.2023. Print 2023 Sep. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 37669858 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeine inhibits hypothalamic A1R to excite oxytocin neuron and ameliorate dietary obesity in mice.Nat Commun. 2017 Jun 27;8:15904. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15904. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28654087 Free PMC article.
-
Nrg4 promotes fuel oxidation and a healthy adipokine profile to ameliorate diet-induced metabolic disorders.Mol Metab. 2017 Jun 21;6(8):863-872. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.03.016. eCollection 2017 Aug. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28752050 Free PMC article.
-
NGR4 and ERBB4 as Promising Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets for Metabolic Disorders.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2023 Jun 6;15(2):14. doi: 10.31083/j.fbe1502014. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2023. PMID: 37369570 Review.
-
A systematic review of the association of neuregulin 4, a brown fat-enriched secreted factor, with obesity and related metabolic disturbances.Obes Rev. 2020 Feb;21(2):e12952. doi: 10.1111/obr.12952. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Obes Rev. 2020. PMID: 31782243
Cited by
-
[Mechanisms by Which Paraventricular Hypothalamic Nucleus Participates in the Acupuncture Treatment of Diseases].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Jan 20;56(1):26-34. doi: 10.12182/20250160202. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40109474 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Energy Expenditure Homeostasis Requires ErbB4, an Obesity Risk Gene, in the Paraventricular Nucleus.eNeuro. 2023 Sep 25;10(9):ENEURO.0139-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0139-23.2023. Print 2023 Sep. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 37669858 Free PMC article.
-
Brown and beige adipose tissue-derived metabokine and lipokine inter-organ signalling in health and disease.Exp Physiol. 2025 Jul;110(7):918-935. doi: 10.1113/EP092008. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Exp Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39591977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of key module and hub genes affecting broiler body weight through weighted gene co-expression network analysis.Poult Sci. 2024 Nov;103(11):104111. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104111. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39153266 Free PMC article.
-
Role of hypothalamus function in metabolic diseases and its potential mechanisms.PeerJ. 2025 May 29;13:e19532. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19532. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40452923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82100908/National Science Foundation of China
- 81974118/National Science Foundation of China
- 82270894/National Science Foundation of China
- 92149306/National Science Foundation of China
- 82200910/National Science Foundation of China
- 20XD1433300/Shanghai Outstanding Academic Leaders
- 21SG11/Shuguang Project
- SHSMU-ZDCX20212700/Innovative research team of high-level local universities in Shanghai
- 2023ZKZD17/Major Natural Science Project of the Scientific Research and Innovation Plan of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Education
- 2022ZZ01002/Shanghai Research Center for Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases
- 2021M700088/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- ynqn202106/Shanghai Sixth People's Hospital Foundation
- Shanghai Municipal Key Clinical Specialty
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
