Comorbid obstructive sleep apnea is associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in female patients with acute coronary syndrome complicating metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 37060185
- PMCID: PMC10270259
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.24020
Comorbid obstructive sleep apnea is associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in female patients with acute coronary syndrome complicating metabolic syndrome
Abstract
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and metabolic syndrome (MetS) are each increasingly common in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Whether OSA increases cardiovascular consequences in ACS patients with MetS has not been investigated.
Hypothesis: OSA increases cardiovascular risk in ACS patients with MetS. We aimed to examine the association between OSA and cardiovascular consequences in ACS patients with MetS.
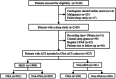
Methods: In this prospective cohort study, we consecutive recruited 2160 ACS patients who underwent portable sleep breathing monitoring. OSA is defined as an apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) ≥ 15 events/h. The primary endpoint was major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (MACCE), including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, ischemia-driven revascularization, or hospitalization for unstable angina or heart failure.
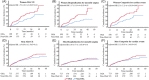
Results: A total of 1927 patients with ACS were enrolled. Among them, 1486 (77.1%) had MetS and 1014 (52.6%) had OSA. During 2.9 years of follow-up, the cumulative incidence of MACCE was similar between OSA and non-OSA groups in patients with MetS (21.9% vs. 17.9%, adjusted hazard ratio [HR] = 1.29 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.99-1.67, p = .06) and patients without MetS (24.4% vs. 17.3%, adjusted HR = 1.21 95% CI: 0.73-2.03, p = .46). Patients with MetS and OSA had a significantly higher risk of MACCE than patients with MetS and without OSA in women (27.8% vs. 18.1%, adjusted HR = 1.70, 95% CI: 1.01-3.09, p = .04) but not in men (21.0% vs. 17.9%, adjusted HR = 1.19, 95% CI: 0.91-1.59, p = .21).
Conclusions: In hospitalized ACS patients with MetS, comorbid OSA was associated with increased risk of cardiovascular consequences among women.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; metabolic syndrome; obstructive sleep apnea.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical Cardiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of obstructive sleep apnea on prognosis in patients with acute coronary syndromes with varying numbers of standard modifiable risk factors: insight from the OSA-ACS study.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2023 Jul;56(1):65-74. doi: 10.1007/s11239-023-02830-w. Epub 2023 May 27. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2023. PMID: 37243941 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Obstructive Sleep Apnea With Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Jan 22;8(2):e010826. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.010826. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 30636505 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of obstructive sleep apnea in patients with acute coronary syndrome in relation to diabetes status.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019 Dec 18;7(1):e000737. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-000737. eCollection 2019. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019. PMID: 31908793 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Obstructive Sleep Apnea With the Risk of Repeat Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Ear Nose Throat J. 2021 May;100(4):260-270. doi: 10.1177/0145561321989450. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021. PMID: 33570429
-
Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular events in acute coronary syndrome: a meta-analysis.Coron Artery Dis. 2023 May 1;34(3):177-184. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000001207. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Coron Artery Dis. 2023. PMID: 36762648
References
-
- Yeghiazarians Y, Jneid H, Tietjens JR, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;144(3):e56‐e67. - PubMed
-
- Bonsignore MR, McNicholas WT, Montserrat JM, Eckel J. Adipose tissue in obesity and obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J. 2012;39(3):746‐767. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

