Rilzabrutinib, a reversible covalent Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor: Absorption, metabolism, excretion, and absolute bioavailability in healthy participants
- PMID: 37060187
- PMCID: PMC10339699
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.13524
Rilzabrutinib, a reversible covalent Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor: Absorption, metabolism, excretion, and absolute bioavailability in healthy participants
Abstract
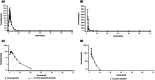
This single-center, open-label, non-randomized, two-part, phase I study was conducted (1) to evaluate the absolute oral bioavailability of rilzabrutinib 400 mg tablet following an i.v. microtracer dose of ~100 μg [14C]-rilzabrutinib (~1 μCi) and single oral dose of 400 mg rilzabrutinib tablet (part 1), and (2) to characterize the absorption, metabolism, and excretion (AME) of 14C-radiolabeled rilzabrutinib following single oral dose (300 mg) of [14C]-rilzabrutinib (~1000 μCi; administered as a liquid) in healthy male participants (part 2). A total of 18 subjects were enrolled (n = 8 in part 1; n = 10 in part 2). The absolute bioavailability of 400 mg rilzabrutinib oral tablet was low (<5%). In part 1, rilzabrutinib was absorbed rapidly after single oral dose of rilzabrutinib 400 mg tablet with a median (range) time to maximum concentration (Tmax ) value of 2.03 h (1.83-2.50 h). The geometric mean (coefficient of variation) terminal half-life following the oral dose and i.v. microtracer dose of ~100 μg [14C]-rilzabrutinib, were 3.20 (51.0%) and 1.78 (37.6%) h, respectively. In part 2, rilzabrutinib was also absorbed rapidly following single oral dose of 300 mg [14C]-rilzabrutinib solution with a median (range) Tmax value of 1.00 h (1.00-2.00 h). The majority of total radioactivity was in the feces for both non-bile collection subjects (92.9%) and bile collection subjects (87.6%), and ~5% of radioactivity was recovered in urine after oral administration. Urinary excretion of unchanged rilzabrutinib was low (3.02%). The results of this study advance the understanding of the absolute bioavailability and AME of rilzabrutinib and can help inform its further investigation.
© 2023 Sanofi. Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
S.U., P.N., J.S., L.L., and J.W. were employees of Principia at the time of the execution of the study and had stock investment from the company. P.F.S. is an employee of Certara and has stock investment from the company. F.L., H.Y., and K.C. are employees of Principia Biopharma (Sanofi company) and have stock investment from the company. M.L. was an employee of Sanofi at the time of the execution of the study and had stock investment from the company.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Phase I Study To Determine the Absolute Bioavailability and Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion of Capivasertib in Healthy Male Participants.Drug Metab Dispos. 2024 Aug 14;52(9):939-948. doi: 10.1124/dmd.124.001636. Drug Metab Dispos. 2024. PMID: 39029948 Clinical Trial.
-
The Absolute Bioavailability and Absorption, Metabolism, and Excretion of Ipatasertib, a Potent and Highly Selective Protein Kinase B (Akt) Inhibitor.Drug Metab Dispos. 2023 Oct;51(10):1332-1341. doi: 10.1124/dmd.122.001175. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Drug Metab Dispos. 2023. PMID: 37524543
-
Open-label, single-center, phase I trial to investigate the mass balance and absolute bioavailability of the highly selective oral MET inhibitor tepotinib in healthy volunteers.Invest New Drugs. 2020 Oct;38(5):1507-1519. doi: 10.1007/s10637-020-00926-1. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Invest New Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32221754 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics, Excretion, and Mass Balance of [14 C]-Batefenterol Following a Single Microtracer Intravenous Dose (Concomitant to an Inhaled Dose) or Oral Dose of Batefenterol in Healthy Men.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2018 Nov;7(8):901-910. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.616. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2018. PMID: 30230263 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of glucosamine sulfate. A review.Arzneimittelforschung. 2001 Sep;51(9):699-725. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1300105. Arzneimittelforschung. 2001. PMID: 11642003 Review.
Cited by
-
IgG4-related digestive diseases: diagnosis and treatment.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 5;14:1278332. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1278332. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37868965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinase Inhibitors and Kinase-Targeted Cancer Therapies: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 17;25(10):5489. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105489. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and future landscape of Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors in allergy.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025 Sep;156(3):568-578. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2025.05.030. Epub 2025 Jun 16. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40532792 Review.
-
Rilzabrutinib in Antihistamine-Refractory Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: The RILECSU Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Dermatol. 2025 Jul 1;161(7):679-687. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2025.0733. JAMA Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40266575 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibition for the treatment of allergic disorders.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024 Jul;133(1):33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2024.03.002. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38492772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

