Propensity score matching analysis of laparoscopic surgery vs. open approach in 4 297 adult patients with acute appendicitis, acute cholecystitis or gastrointestinal tract perforation: a prospective multicentre study of nationwide outcomes
- PMID: 37060247
- PMCID: PMC10389196
- DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000384
Propensity score matching analysis of laparoscopic surgery vs. open approach in 4 297 adult patients with acute appendicitis, acute cholecystitis or gastrointestinal tract perforation: a prospective multicentre study of nationwide outcomes
Abstract
Background and aims: Previous studies indicated that laparoscopic surgery could improve postoperative outcomes in acute appendicitis, acute cholecystitis, perforated gastroduodenal ulcer, or acute diverticulitis, but some reported opposite results or differences in the magnitude of improvement. A contemporary analysis using propensity score matching that compares outcomes is lacking.
Methods: Over a 6-month period, 38 centres (5% of all public hospitals) attending emergency general surgery patients on a 24 h, 7 days a week basis, enroled all consecutive adult patients who underwent laparoscopic surgery or open approach.
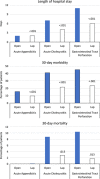
Results: The study included 2 645 patients with acute appendicitis [32 years (22-51), 44.3% women], 1 182 with acute cholecystitis [65 years (48-76); 46.7% women], and 470 with gastrointestinal tract perforation [65 years (50-76); 34% women]. After propensity score matching, hospital stays decreased in acute appendicitis [open, 2 days (2-4); lap, 2 days (1-4); P <0.001], acute cholecystitis [open, 7 days (4-12); lap, 4 days (3-6); P <0.001], and gastrointestinal tract perforation [open, 11 days (7-17); lap, 6 days (5-8.5); P <0.001]. A decrease in 30-day morbidity was observed in acute appendicitis (open, 15.7%; lap, 9.7%; P <0.001), acute cholecystitis (open, 41%; lap, 21.7%; P <0.001), and gastrointestinal tract perforation (open, 45.2%; lap, 23.5%; P <0.001). A decrease in 30-day mortality was found in acute cholecystitis (open, 8.8%; lap, 2.8%; P =0.013) and gastrointestinal tract perforation (open, 10.4%; lap, 1.7%; P =0.013).
Conclusions: This clinically based, multicentre study suggests that an initial laparoscopic approach could be considered not only in patients with acute appendicitis or acute cholecystitis but also in patients with a perforation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart B, Khanduri P, McCord C, et al. . Global disease burden of conditions requiring emergency surgery. Br J Surg 2014;101:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Wickramasinghe DP, Xavier C, Samarasekera DN. The worldwide epidemiology of acute appendicitis: an analysis of the global health data exchange dataset. World J Surg 2021;45:1999–2008. - PubMed
-
- Coccolini F, Catena F, Pisano M, et al. . Open versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy in acute cholecystitis. Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg 2015;18:196–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

