A universal fluorescence polarization high throughput screening assay to target the SAM-binding sites of SARS-CoV-2 and other viral methyltransferases
- PMID: 37060263
- PMCID: PMC10165934
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2204164
A universal fluorescence polarization high throughput screening assay to target the SAM-binding sites of SARS-CoV-2 and other viral methyltransferases
Abstract
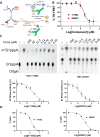
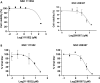
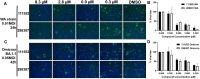
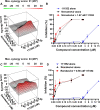
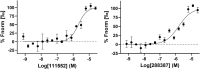
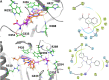
SARS-CoV-2 has caused a global pandemic with significant humanity and economic loss since 2020. Currently, only limited options are available to treat SARS-CoV-2 infections for vulnerable populations. In this study, we report a universal fluorescence polarization (FP)-based high throughput screening (HTS) assay for SAM-dependent viral methyltransferases (MTases), using a fluorescent SAM-analogue, FL-NAH. We performed the assay against a reference MTase, NSP14, an essential enzyme for SARS-CoV-2 to methylate the N7 position of viral 5'-RNA guanine cap. The assay is universal and suitable for any SAM-dependent viral MTases such as the SARS-CoV-2 NSP16/NSP10 MTase complex and the NS5 MTase of Zika virus (ZIKV). Pilot screening demonstrated that the HTS assay was very robust and identified two candidate inhibitors, NSC 111552 and 288387. The two compounds inhibited the FL-NAH binding to the NSP14 MTase with low micromolar IC50. We used three functional MTase assays to unambiguously verified the inhibitory potency of these molecules for the NSP14 N7-MTase function. Binding studies indicated that these molecules are bound directly to the NSP14 MTase with similar low micromolar affinity. Moreover, we further demonstrated that these molecules significantly inhibited the SARS-CoV-2 replication in cell-based assays at concentrations not causing cytotoxicity. Furthermore, NSC111552 significantly synergized with known SARS-CoV-2 drugs including nirmatrelvir and remdesivir. Finally, docking suggested that these molecules bind specifically to the SAM-binding site on the NSP14 MTase. Overall, these molecules represent novel and promising candidates to further develop broad-spectrum inhibitors for the management of viral infections.
Keywords: NSP14; SARS-CoV-2; high throughput screening; inhibitor; methyltransferase.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
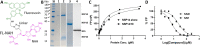

Similar articles
-
Synthesis of adenine dinucleosides SAM analogs as specific inhibitors of SARS-CoV nsp14 RNA cap guanine-N7-methyltransferase.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Sep 1;201:112557. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112557. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32563813 Free PMC article.
-
Broad-Spectrum Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the SAM-Binding Site of Flavivirus NS5 Methyltransferase.ACS Infect Dis. 2023 Jul 14;9(7):1319-1333. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.2c00571. Epub 2023 Jun 22. ACS Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37348028 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and structural insights into the mechanisms of SARS coronavirus RNA ribose 2'-O-methylation by nsp16/nsp10 protein complex.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002294. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002294. Epub 2011 Oct 13. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22022266 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus 2'-O-methyltransferase: A promising therapeutic target.Virus Res. 2023 Oct 15;336:199211. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199211. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 37634741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavivirus methyltransferase: a novel antiviral target.Antiviral Res. 2008 Oct;80(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.05.003. Epub 2008 Jun 5. Antiviral Res. 2008. PMID: 18571739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a luminescence-based method for measuring West Nile Virus MTase activity and its application to screen for antivirals.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2024 Oct 2;7:100282. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2024.100282. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2024. PMID: 39445035 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons learnt from broad-spectrum coronavirus antiviral drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2024 Sep;19(9):1023-1041. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2024.2385598. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39078037 Review.
-
An ISG15-Based High-Throughput Screening Assay for Identification and Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors Targeting Papain-like Protease.Viruses. 2024 Aug 1;16(8):1239. doi: 10.3390/v16081239. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39205213 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Methyltransferase Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 and nsp16.Molecules. 2024 May 15;29(10):2312. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102312. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38792173 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 NSP14 MTase activity is critical for inducing canonical NF-κB activation.Biosci Rep. 2024 Jan 31;44(1):BSR20231418. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231418. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38131452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Owen DR, Allerton CMN, Anderson AS, et al. . An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science. 2021 Dec 24;374(6575):1586–1593. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
