Research on synergistic erosion by cavitation and sediment: A review
- PMID: 37060709
- PMCID: PMC10139983
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106399
Research on synergistic erosion by cavitation and sediment: A review
Abstract
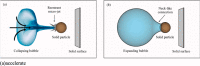
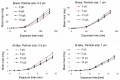
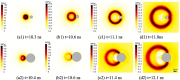
Sediment erosion frequently occurs in areas with high incidences of cavitation. The collaborative impact of abrasion and cavitation presents a host of challenges, threats, and damages to hydraulic engineering. However, little is known about the synergistic wear mechanism, and research conclusions remain inconsistent. In this work, relevant studies on synergistic erosion have been collected, classified, and analyzed. Presently, research on synergistic wear primarily operates at the macro and micro levels. The microscopic level enables the visualization and quantification of the process by which particles gain momentum from bubbles, the trajectory of particle acceleration, and the mechanism that triggers strong interactions between bubble-particle. At the macro level, erosion is understood as the summation of damage effects on the wall that is caused by the interaction between a plethora of bubbles of varying scales and numerous particles. The synergistic bubble-particle effect is reflected in the dual inhibiting or promoting mechanism. Furthermore, while numerical simulations could be realized by coupling cavitation, multiphase flow, and erosion models, their accuracy is not infallible. In the future, the dual role of particles, and particles driven by micro-jets or shock waves should be fully considered when establishing a combined erosion model. In addition, enhancing the influence of flow field and boundary parameters around bubbles and utilizing FSI would improve the predictive accuracy of erosion location and erosion rate. This work helps to elucidate the combined wear mechanism of hydraulic machinery components in sediment-laden flow environments and provides a theoretical basis for the design, manufacture, processing, and maintenance of hydraulic machinery.
Keywords: Cavitation damage; Dual mechanism; Numerical techniques; Particle erosion; Synergistic effect.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




















Similar articles
-
Experimental study on the mesoscale causes of the influence of viscosity on material erosion in a cavitation field.Ultrason Sonochem. 2019 Dec;59:104699. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104699. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Ultrason Sonochem. 2019. PMID: 31476699
-
Numerical study of the synergistic effect of cavitation and micro-abrasive particles.Ultrason Sonochem. 2022 Sep;89:106119. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106119. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Ultrason Sonochem. 2022. PMID: 35969914 Free PMC article.
-
An equivalent method of jet impact loading from collapsing near-wall acoustic bubbles: A preliminary study.Ultrason Sonochem. 2021 Nov;79:105760. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105760. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Ultrason Sonochem. 2021. PMID: 34653916 Free PMC article.
-
Silt erosion and cavitation impact on hydraulic turbines performance: An in-depth analysis and preventative strategies.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 5;10(8):e28998. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28998. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38644884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bubbles with shock waves and ultrasound: a review.Interface Focus. 2015 Oct 6;5(5):20150019. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2015.0019. Interface Focus. 2015. PMID: 26442143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Control mechanisms of different bionic structures for hydrofoil cavitation.Ultrason Sonochem. 2024 Jan;102:106745. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106745. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Ultrason Sonochem. 2024. PMID: 38163405 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of 3.5 % NaCl solution with different Na2S concentrations on ultrasonic cavitation erosion behaviors of HVOF sprayed WC-Ni coatings.Ultrason Sonochem. 2023 Dec;101:106707. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106707. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023. PMID: 38039594 Free PMC article.
-
Jet dynamics of a cavitation bubble near unequal-sized dual particles.Ultrason Sonochem. 2024 Jul;107:106942. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.106942. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Ultrason Sonochem. 2024. PMID: 38850641 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental and numerical research on jet dynamics of cavitation bubble near dual particles.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 Jan;112:107168. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.107168. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 39571496 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the dynamic characteristics of the cavitation bubble collapsing between multiple particles.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 Jan;112:107169. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.107169. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 39577065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuriqi A., Pinheiro A.N., Sordo-Ward A., Bejarano M.D., Garrote L. Ecological impacts of run-of-river hydropower plants—Current status and future prospects on the brink of energy transition. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021;142
-
- Gernaat D.E.H.J., Bogaart P.W., van Vuuren D.P., Biemans H., Niessink R. High-resolution assessment of global technical and economic hydropower potential. Nat. Energy. 2017;2:821–828.
-
- Killingtveit Å. In: Future Energy (Third Edition) Letcher T.M., editor. Elsevier; 2020. 15 - Hydroelectric Power; pp. 315–330.
-
- Noon A.A., Kim M.-H. Sediment and Cavitation Erosion in Francis Turbines—Review of Latest Experimental and Numerical Techniques. Energies. 2021;14:1516.
-
- Mei Z., Wu Y. In: Hydraulic Machinery and Cavitation. Cabrera E., Espert V., Martínez F., editors. Springer; Netherlands, Dordrecht: 1996. Review of Research on Abrasion and Cavitation of Silt-Laden Flows Through Hydraulic Turbines in China; pp. 641–650.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

