Short-term exposure to some heavy metals carried with PM10 and cardiovascular system biomarkers during dust storm
- PMID: 37061544
- PMCID: PMC10105359
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-31978-x
Short-term exposure to some heavy metals carried with PM10 and cardiovascular system biomarkers during dust storm
Abstract
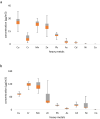
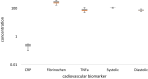
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of short-term exposure to heavy metals (HM) extracted from PM10 on CB in workers' population in an outdoor space located in southern Iran during a dust storm. At first, 44 healthy and non-smoking workers were selected. Then PM10 and Blood samples were collected before and after the dust storm. Finally, HMs associated with PM10 measured by ICP-MS and its effect on the CB, including fibrinogen, CRP, TNF-α, and BP were estimated by ANOVA, Pearson correlation, and Odd Ratio (OR) in SPSS23. Based on the results, the concentration of PM10 and extracted HM such as Cr, As, and Cd was higher than the WHO/EPA standards in dust storms they increased the CB and BP remarkably. Moreover, the level of fibrinogen, blood pressure (BP) and TNF-α in dust storms were higher than in normal conditions (p < 0.05, OR > 3). In addition, As and Cd decreased fibrinogen concentration and systolic BP, respectively. Whereas, TNF-α was associated with concentration of Pb (R = - 0.85) on normal days. Consequently, the HM on PM10 such as As, interferes with the level of investigated CB. These results considered a potential risk for the residents in the southern regions of Iran.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Atmospheric Particulate Matter and Dust].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2017 Sep 8;38(9):3575-3584. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201702054. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2017. PMID: 29965235 Chinese.
-
Concentration, contamination level, source identification of selective trace elements in Shiraz atmospheric dust sediments (Fars Province, SW Iran).Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Mar;26(7):6424-6435. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-04100-2. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30623330
-
Elemental and carbonaceous characterization of TSP and PM10 during Middle Eastern dust (MED) storms in Ahvaz, Southwestern Iran.Environ Monit Assess. 2017 Aug 21;189(9):462. doi: 10.1007/s10661-017-6182-1. Environ Monit Assess. 2017. PMID: 28828754
-
Pollution status and human health risk assessments of selected heavy metals in urban dust of 16 cities in Iran.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jun;27(18):23094-23107. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08585-8. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32329009 Review.
-
Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018.Environ Int. 2019 Jul;128:430-437. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.04.046. Epub 2019 May 10. Environ Int. 2019. PMID: 31082721 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene Expression and Metabolome Analysis Reveals Anti-Inflammatory Impacts of 11,17diHDoPE on PM10-Induced Mouse Lung Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 14;25(10):5360. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105360. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791399 Free PMC article.
-
Heavy Metals Content and Health Risk Assessment in Airborne Particulate from the Calabria Region, Southern Italy.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Mar 31;21(4):426. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21040426. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38673337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heidari-Farsani M, Shirmardi M, Goudarzi G, Alavi-Bakhtiarivand N, Ahmadi-Ankali K, Zallaghi E, et al. The evaluation of heavy metals concentration related to PM10 in ambient air of Ahvaz city Iran. J. Adv. Environ. Health Res. 2013;1(2):120–128.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

