Telocytes and ezrin expression in normal-appearing tissues adjacent to urothelial bladder carcinoma as predictors of invasiveness and recurrence
- PMID: 37061568
- PMCID: PMC10105776
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-33282-0
Telocytes and ezrin expression in normal-appearing tissues adjacent to urothelial bladder carcinoma as predictors of invasiveness and recurrence
Abstract
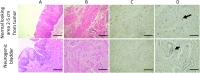
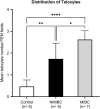
Recurrence and progression rates vary widely among different histological subtypes of bladder cancer (BC). Normal-appearing mucosa in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer and muscle-invasive bladder cancer in cystoscopy and histopathology is a factor in staging and treatment. Telocytes (TCs) are spindle-shaped cells that connect with other cell types allowing communication though cytoskeletal signaling. They are involved in tissue regeneration and pathogenesis of diseases and cancer. In this study, 12 normal-appearing tissues from urinary bladder with BC, both invasive and non-invasive were evaluated in patients who had either trans-urethral resection of bladder tumor or cystectomy. In each case, cystoscopy, intraoperative inspection, and histopathology all confirmed the absence of cancerous elements. Five patients with neurogenic bladder were used as a control group. Immunohistochemistry revealed that c-Kit + cells were intensively distributed in bladder layers from BC samples, while they were seldom detected in the control group. Ultrastructural examination of reprocessed tissue showed an intense distribution of TCs and telopodes in the submucosa and between smooth muscle cells in BC. Telopodes were numerous, arborizing, and intercommunicating. Whereas TCs and telopodes were scarce in the neurogenic bladder. Also, cancerous tissue had the highest expression level of ezrin protein, and this level gradually decreased as we moved away from the tumor. Our finding of TCs number in normal-appearing tissues in conjunction with ezrin expression may compete invasiveness and possibly a trail to reduce recurrence rates.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
EAU Guidelines on Non-Muscle-invasive Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder: Update 2016.Eur Urol. 2017 Mar;71(3):447-461. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.041. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 27324428
-
Some pitfalls in pathological staging of invasive urothelial carcinoma.J Urol. 2004 Oct;172(4 Pt 1):1464. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000139963.82030.0b. J Urol. 2004. PMID: 15371871 No abstract available.
-
Preoperative predictive factors of carcinoma in situ in the normal-appearing mucosa in patients who underwent an initial transurethral resection for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer under white light cystoscopy.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2021 Apr;4(2):e1321. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1321. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 33174397 Free PMC article.
-
Management of high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2012 Dec;64(4):255-60. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2012. PMID: 23288212 Review.
-
New optical imaging technologies for bladder cancer: considerations and perspectives.J Urol. 2012 Aug;188(2):361-8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.03.127. Epub 2012 Jun 13. J Urol. 2012. PMID: 22698620 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Telocytes of the male reproductive system: dynamic tissue organizers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 14;12:1444156. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1444156. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39469114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NR4A3 regulates anoikis resistance and metastasis of bladder cancer through EWSR1.Cancer Biol Ther. 2025 Dec;26(1):2535774. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2025.2535774. Epub 2025 Aug 5. Cancer Biol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40762284 Free PMC article.
-
Is bladder outlet obstruction rat model to induce overactive bladder (OAB) has similarity to human OAB? Research on the events in smooth muscle, collagen, interstitial cell and telocyte distribution.BMC Res Notes. 2024 Jan 11;17(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13104-023-06681-9. BMC Res Notes. 2024. PMID: 38212840 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Telocytes and inflammation: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 17;102(46):e35983. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035983. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37986278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Cancer today. http://gco.iarc.fr/today/home.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

