Bleeding related to oral anticoagulants: Trends in US emergency department visits, 2016-2020
- PMID: 37062120
- PMCID: PMC10870325
- DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2023.03.010
Bleeding related to oral anticoagulants: Trends in US emergency department visits, 2016-2020
Abstract
Background: Clinical trials suggest lower rates of major bleeding with direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs) than with warfarin, but anticoagulant-related bleeding remains one of the most common outpatient adverse drug events.
Methods: We estimated the number of emergency department (ED) visits and subsequent hospitalizations for oral anticoagulant-related bleeding in 2016-2020 based on active surveillance in a nationally representative, size-stratified probability sample of 60 U.S. hospitals. We estimated rates of ED visits using a nationally-projected retail prescription dispensing database.
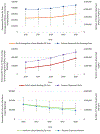
Results: Based on 19,557 cases, oral anticoagulant-related bleeding resulted in an estimated 1,270,259 (95 % Confidence Interval [CI], 644,686-1,895,832) ED visits for the five years 2016-2020, of which 47.8 % (95 % CI, 40.6 %-55.0 %) resulted in hospitalization. Oral anticoagulant-related bleeding resulted in an estimated 230,163 (95% CI, 109,598-350,728) ED visits in 2016 and 301,433 (95% CI, 138,363-464,503) in 2020. During 2016-2020, ED visits for DOAC-related bleeding increased by an average of 27.9 % (95 % CI, 24.0 %-32.0 %; p < .001) per year, while ED visits for warfarin-related bleeding decreased by an average of 8.8 % (95 % CI, -10.7 % to -7.0 %; p = .001) per year. The estimated rate of bleeding visits per 100 patients dispensed oral anticoagulants at least once in 2016-2020 was highest for patients aged ≥ 80 years (13.1; 95 % CI, 6.2-20.0) and lowest for those aged <45 years (4.0; 95 % CI, 2.6-5.5); it was 5.9 visits per 100 patients dispensed DOACs [95 % CI, 2.5-9.2] and 13.0 visits per 100 patients dispensed warfarin [95 % CI, 7.4-18.7].
Conclusions: Although the rates of ED visits for anticoagulant-related bleeding may be lower for DOACs than for warfarin, persistently large numbers of patients requiring ED visits for anticoagulant-related bleeding despite increased use of DOACs and declining use of warfarin suggest that efforts to improve appropriate prescribing and monitoring of anticoagulants remain important.
Keywords: Adverse drug events; Anticoagulant-related bleeding; Oral anticoagulants; Pharmaceutical safety; Public health surveillance.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Budnitz DS, Pollock DA, Weidenbach KN, Mendelsohn AB, Schroeder TJ, Annest JL. National surveillance of emergency department visits for outpatient adverse drug events. JAMA. 2006;296(15):1858–1866. - PubMed
-
- Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139–1151. - PubMed
-
- Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(11):981–992. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

