Neural Correlates of the p Factor in Adolescence: Cognitive Control With and Without Enhanced Positive Affective Demands
- PMID: 37062361
- PMCID: PMC10576014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2023.03.012
Neural Correlates of the p Factor in Adolescence: Cognitive Control With and Without Enhanced Positive Affective Demands
Abstract
Background: Recent research has aimed to characterize processes underlying general liability toward psychopathology, termed the p factor. Given previous research linking the p factor with difficulties in both executive functioning and affective regulation, the present study investigated nonaffective and positive affective inhibition in the context of a sustained attention/inhibition paradigm in adolescents exhibiting mild to severe psychopathology.
Methods: Functional magnetic resonance imaging data were collected during an integrated reward conditioning and go/no-go task in 138 adolescents assigned female at birth. We modeled the p factor using hierarchical confirmatory factor analysis. Positive affective inhibition was measured by examining responses to no-go stimuli with a history of reward conditioning. We examined associations between p factor scores and neural function and behavioral performance.
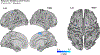
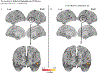
Results: Consistent with nonaffective executive function as a primary risk factor, p factor scores were associated with worse behavioral performance and hypoactivation in the left superior frontal gyrus and middle frontal gyrus during response initiation (go trials). The p factor scores were additionally associated with increased error-related signaling in the temporal cortex during incorrect no-go trials.
Conclusions: During adolescence, a period characterized by heightened risk for emergent psychopathology, we observed unique associations between p factor scores and neural and behavioral indices of response initiation, which relies primarily on sustained attention. These findings suggest that shared variation in mental disorder categories is characterized in part by sustained attention deficits. While we did not find evidence that the p factor was associated with inhibition in this study, this observation is consistent with our hypothesis that the p factor would be related to nonaffective control processes.
Keywords: Adolescence; Go/no-go task; Inhibition; Psychopathology; Sustained attention; p factor.
Copyright © 2023 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Achenbach TM (1991): Manual for the child behavior checklist/4–18 and 1991 profile. Burlington VT: University of Vermont.
-
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE (2005): Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archives of General Psychiatry 62: 593–602. - PubMed

