A Computational Model Reveals Learning Dynamics During Interpretation Bias Training With Clinical Applications
- PMID: 37062362
- PMCID: PMC10576009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2023.03.013
A Computational Model Reveals Learning Dynamics During Interpretation Bias Training With Clinical Applications
Abstract
Background: Some psychopathologies, including anxiety and irritability, are associated with biases when judging ambiguous social stimuli. Interventions targeting these biases, or interpretation bias training (IBT), are amenable to computational modeling to describe their associative learning mechanisms. Here, we translated ALCOVE (attention learning covering map), a model of category learning, to describe learning in youths with affective psychopathology when training on more positive judgments of ambiguous face emotions.
Methods: A predominantly clinical sample comprised 71 youths (age range, 8-22 years) representing broad distributions of irritability and anxiety symptoms. Of these, 63 youths were included in the test sample by completing an IBT task with acceptable performance for computational modeling. We used a separate sample of 28 youths to translate ALCOVE for individual estimates of learning rate and generalization. In the test sample, we assessed associations between model learning estimates and irritability, anxiety, their shared variance (negative affectivity), and age.
Results: Age and affective symptoms were associated with category learning during IBT. Lower learning rates were associated with higher negative affectivity common in anxiety and irritability. Lower generalization, or improved discrimination between face emotions, was associated with increasing age.
Conclusions: This work demonstrates a functional consequence of age- and symptom-related learning during interpretation bias. Learning measured by ALCOVE also revealed learning types not accounted for in the prior literature on IBT. This work more broadly demonstrates the utility of measurement models for understanding trial-by-trial processes and identifying individual learning styles.
Keywords: Anxiety; Category learning; Cognitive bias modification; Interpretation bias training; Irritability.
Copyright © 2023 Society of Biological Psychiatry. All rights reserved.
Figures

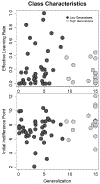

Similar articles
-
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of a computer-based Interpretation Bias Training for youth with severe irritability: a study protocol.Trials. 2018 Nov 14;19(1):626. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2960-5. Trials. 2018. PMID: 30428909 Free PMC article.
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial of Computerized Interpretation Bias Training for Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder: A Fast-Fail Study.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2022 Jan;61(1):37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2021.05.022. Epub 2021 Jun 17. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 34147585 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Attention bias to negative versus non-negative faces is related to negative affectivity in a transdiagnostic youth sample.J Psychiatr Res. 2021 Jun;138:514-518. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.04.036. Epub 2021 May 1. J Psychiatr Res. 2021. PMID: 33975068 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Eye-Tracking of Attention to Threat in Child and Adolescent Anxiety.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020 Jan;59(1):88-99.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2019.06.006. Epub 2019 Jun 29. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31265874
-
A systematic review of treatments targeting cognitive biases in socially anxious adolescents: Special Section on "Translational and Neuroscience Studies in Affective Disorders" Section Editor, Maria Nobile MD, PhD.J Affect Disord. 2020 Mar 1;264:543-551. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.12.002. Epub 2019 Dec 3. J Affect Disord. 2020. PMID: 32056778 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Chronotype and emotion processing: a pilot study testing timing of online cognitive bias modification training.BMJ Ment Health. 2024 Jul 2;27(1):1-7. doi: 10.1136/bmjment-2024-301045. BMJ Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 38960412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crick NR & Dodge KA. (1994). A review and reformulation of social information-processing mechanisms in children’s social adjustment. Psychological Bulletin, 115(1), 74.
-
- Mathews A & MacLeod C. (1994). Cognitive approaches to emotion and emotional disorders. Annual Review of Psychology, 45(1), 25–50. - PubMed
-
- Smith HL, Summers BJ, Dillon KH, Macatee RJ, & Couglen JR. (2016). Hostile interpretation bias in depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 203, 9–13. - PubMed
-
- Haller SP, Stoddard J, Botz-Zapp C, Clayton M, MacGillivray C, Perhamus G, et al. (2022). A randomized controlled trial of computerized interpretation bias training for disruptive mood dysregulation disorder: A fast-fail study. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 61(1), 37–45. - PMC - PubMed

