Gasdermins gone wild: new roles for GSDMs in regulating cellular homeostasis
- PMID: 37062616
- PMCID: PMC10611448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.02.007
Gasdermins gone wild: new roles for GSDMs in regulating cellular homeostasis
Abstract
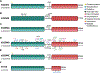
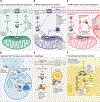
Since their discovery, members of the gasdermin (GSDM) family of proteins have been firmly established as executors of pyroptosis, with the N-terminal fragment of most GSDMs capable of forming pores in the plasma membrane. More recent findings suggest that some GSDMs can drive additional cell death pathways, such as apoptosis and necroptosis, through mechanisms independent of plasma membrane perforation. There is also emerging evidence that by associating with cellular compartments such as mitochondria, peroxisomes, endosomes, and the nucleus, GSDMs regulate cell death-independent aspects of cellular homeostasis. Here, we review the diversity of GSDM function across several cell types and explore how various cellular stresses can promote relocalization - and thus refunctionalization - of GSDMs.
Keywords: ROS; cardiolipin; cell death–independent gasdermin function; mitochondria; oxidative stress; peroxisomes; phospholipids.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Pyroptotic and Nonpyroptotic Roles of Gasdermins in Modulating Cancer Progression and Their Perspectives on Cancer Therapeutics.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2023 May 31;71(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s00005-023-00678-9. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2023. PMID: 37258998 Review.
-
Epigenetic and transcriptional control of gasdermins.Semin Immunol. 2023 Nov;70:101841. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101841. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Semin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37703611 Review.
-
Gasdermins: New Therapeutic Targets in Host Defense, Inflammatory Diseases, and Cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 1;13:898298. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.898298. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To die or not to die: Gasdermins in intestinal health and disease.Semin Immunol. 2024 Feb;71:101865. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2024.101865. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Semin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38232665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and structural aspects of gasdermin family pores and insights into gasdermin-elicited programmed cell death.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Dec 17;49(6):2697-2710. doi: 10.1042/BST20210672. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34812891 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Pyroptosis in Endometrial Cancer and Its Therapeutic Regulation.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct 3;17:7037-7056. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S486878. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39377044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gasdermin D-mediated metabolic crosstalk promotes tissue repair.Nature. 2024 Oct;634(8036):1168-1177. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08022-7. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39260418
-
GSDMD Deficiency Attenuates the Development of Ascending Aortic Dissections in a Novel Mouse Model.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025 Apr;45(4):541-556. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.321740. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025. PMID: 39945067
-
Pyroptosis: A spoiler of peaceful coexistence between cells in degenerative bone and joint diseases.J Adv Res. 2025 May;71:227-262. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.06.010. Epub 2024 Jun 13. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38876191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mast cells boost anti-tumor potency of MAIT cells via inflammasome-dependent secretion of IL-18.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 2;16(1):6074. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61324-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40603850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martinon F et al. (2002) The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell 10 (2), 417–26. - PubMed
-
- Kayagaki N et al. (2021) NINJ1 mediates plasma membrane rupture during lytic cell death. Nature 591 (7848), 131–136. - PubMed
-
- Tamura M et al. (2007) Members of a novel gene family, Gsdm, are expressed exclusively in the epithelium of the skin and gastrointestinal tract in a highly tissue-specific manner. Genomics 89 (5), 618–29. - PubMed
-
- Saeki N et al. (2009) Distinctive expression and function of four GSDM family genes (GSDMA-D) in normal and malignant upper gastrointestinal epithelium. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 48 (3), 261–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

