Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with an increased incidence of chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- PMID: 37062837
- PMCID: PMC10108448
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-023-01114-6
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with an increased incidence of chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the leading cause of chronic liver disease in the western world. The excess mortality in NAFLD patients is strongly related to extrahepatic comorbidities. Recently, an association between NAFLD and chronic kidney disease (CKD) has been reported in various populations.
Methods: Based on the IQVIA Disease Analyzer database, this retrospective study examined two cohorts from Germany matched for sex, age, index year, annual visit frequency, hypertension, and diabetes, including 92,225 patients with and without NAFLD. The incidence of CKD was assessed as a function of NAFLD using Cox regression models.
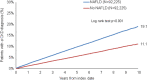
Results: A total of 92,225 NAFLD patients as well as 92,225 patients without NAFLD were included into analyses. CKD was diagnosed in 19.1% vs. 11.1% of patients with and without NAFLD within the 10 years observation period (p < 0.001). Cox regression confirmed a significant association between NAFLD and CKD with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.80 (95%CI: 1.73-1.86, p < 0.001). Subgroup analyses revealed that this association was most pronounced in the age group of 18 to 50 years (HR: 2.13, 95%CI: 1.91-2.37, p < 0.001) and among female NAFLD patients (HR 1.85, 95%CI: 1.76-1.95, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The results of this study confirm a significantly increased risk of developing CKD in a large, real-world cohort of adult NAFLD patients in Germany. Interdisciplinary care of NAFLD patients, which is currently gaining importance worldwide, should be considered to include systematic measures for prevention and/or early detection of CKD with the aim of minimizing long-term renal complications.
Keywords: CKD; Chronic kidney disease; Epidemiology; Metabolic syndrome; NAFLD; NASH; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease increases the risk of incident chronic kidney disease.United European Gastroenterol J. 2020 Oct;8(8):942-948. doi: 10.1177/2050640620944098. Epub 2020 Jul 23. United European Gastroenterol J. 2020. PMID: 32698692 Free PMC article.
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and clinical outcomes in chronic kidney disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019 Mar 1;34(3):449-457. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx381. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019. PMID: 29390103
-
Increased mortality in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with chronic kidney disease is explained by metabolic comorbidities.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019 Oct;43(5):542-550. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30827925
-
A brief review on the rising incidence of chronic kidney diseases and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Physiol Int. 2019 Dec 1;106(4):305-310. Physiol Int. 2019. PMID: 31906711 Review.
-
MAFLD and CKD: An Updated Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 23;23(13):7007. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137007. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806010 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Underdiagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with a Documented Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate and/or Urine Albumin-Creatinine Ratio in Germany.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 May 2;61(5):843. doi: 10.3390/medicina61050843. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40428801 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a nomogram for detecting chronic kidney disease in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Insights from the NHANES database.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2025 May 7;80:100686. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100686. eCollection 2025. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2025. PMID: 40339352 Free PMC article.
-
Epicardial and liver fat implications in albuminuria: a retrospective study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Aug 22;23(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02399-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39175063 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of Lactobacillus casei and Chlorella vulgaris in high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)-associated kidney damages: a stereological study.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 May 5;51(1):613. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09542-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38704764
-
Association between liver fibrosis scores and short-term clinical outcomes in hospitalized chronic kidney disease patients: a prospective observational study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 20;11:1387472. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1387472. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39228803 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical