RPL21 interacts with LAMP3 to promote colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by regulating focal adhesion formation
- PMID: 37062845
- PMCID: PMC10108486
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-023-00443-y
RPL21 interacts with LAMP3 to promote colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by regulating focal adhesion formation
Abstract
Background: Metastasis is the leading cause of death among patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). Therefore, it is important to explore the molecular mechanisms of metastasis to develop effective therapeutic targets for CRC. In the present study, ribosomal protein L21 (RPL21) was considered as being involved in promoting CRC metastasis, yet the underlying mechanism requires further investigation.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry, western blotting, and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction were performed to measure the expression of RPL21 and lysosome-associated membrane protein 3 (LAMP3) in CRC tissues and cells. Wound healing, transwell migration, and invasion assays were performed to study the migration and invasion of cultured CRC cells. An orthotopic CRC mouse model was developed to investigate the metastatic ability of CRC. Transcriptome sequencing was conducted to identify the genes related to RPL21. The dual-luciferase reporter gene assay was performed to determine the transcriptional activity of transcription factor EB (TFEB). The GST/His pull-down assay was performed to investigate the specific binding sites of RPL21 and LAMP3. The cell adhesion assay was performed to determine the adhesion ability of CRC cells. Immunofluorescence staining was performed to observe focal adhesions (FAs).
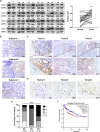
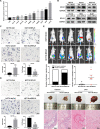
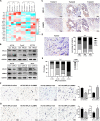
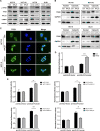
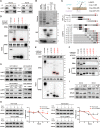
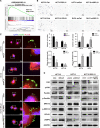
Results: RPL21 was highly expressed in CRC, contributing to tumor invasiveness and poor patient prognosis. Functionally, RPL21 promoted the migration and invasion of CRC cells in vitro and tumor metastasis in vivo. Moreover, LAMP3 was identified as being highly related to RPL21 and was essential in promoting the migration and invasion of CRC cells. Mechanistically, RPL21 activated the transcriptional function of TFEB to upregulate LAMP3 expression. RPL21 directly bound to the aa 341-416 domain of LAMP3 via its aa 1-40 and aa 111-160 segments. The combination of RPL21 and LAMP3 enhanced the stability of the RPL21 protein by suppressing the degradation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Furthermore, RPL21 and LAMP3 promoted the formation of immature FAs by activating the FAK/paxillin/ERK signaling pathway.
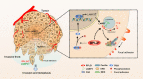
Conclusions: RPL21 promoted invasion and metastasis by regulating FA formation in a LAMP3-dependent manner during CRC progression. The interaction between RPL21 and LAMP3 may function as a potential therapeutic target against CRC.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Focal adhesion; Invasion; LAMP3; Metastasis; Migration; RPL21; TFEB.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

