Mitochondrial redox system: A key target of antioxidant therapy to prevent acquired sensorineural hearing loss
- PMID: 37063286
- PMCID: PMC10102650
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1176881
Mitochondrial redox system: A key target of antioxidant therapy to prevent acquired sensorineural hearing loss
Abstract
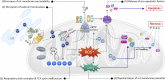
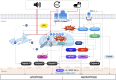
Noise (noise-induced hearing loss), and ototoxic drugs (drug-induced ototoxicity), and aging (age-related hearing loss) are the major environmental factors that lead to acquired sensorineural hearing loss. So far, there have been numerous efforts to develop protective or therapeutic agents for acquired hearing loss by investigating the pathological mechanisms of each types of hearing loss, especially in cochlear hair cells and auditory nerves. Although there is still a lack of information on the underlying mechanisms of redox homeostasis and molecular redox networks in hair cells, an imbalance in mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels that enhance oxidative stress has been suggested as a key pathological factor eventually causing acquired sensorineural hearing loss. Thus, various types of antioxidants have been investigated for their abilities to support auditory cells in maintenance of the hearing function against ototoxic stimuli. In this review, we will discuss the scientific possibility of developing drugs that target particular key elements of the mitochondrial redox network in prevention or treatment of noise- and ototoxic drug-induced hearing loss.
Keywords: ROS; acquired hearing loss; drug development; mitochondria; noise; ototoxic drugs.
Copyright © 2023 Baek, Kim, Lee and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Baumgartner J. E., Baumgartner L. S., Baumgartner M. E., Moore E. J., Messina S. A., Seidman M. D., et al. (2021). Progenitor cell therapy for acquired pediatric nervous system injury: Traumatic brain injury and acquired sensorineural hearing loss. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 10, 164–180. 10.1002/sctm.20-0026 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

