Attenuating lipid metabolism in atherosclerosis: The potential role of Anti-oxidative effects on low-density lipoprotein of herbal medicines
- PMID: 37063287
- PMCID: PMC10102431
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1161657
Attenuating lipid metabolism in atherosclerosis: The potential role of Anti-oxidative effects on low-density lipoprotein of herbal medicines
Abstract
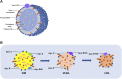
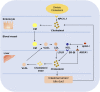
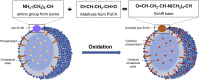
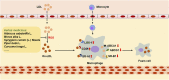
Atherosclerosis (AS) is a multifactorial chronic disease with great harm to the health of human being, which is a basic pathogenesis of many cardiovascular diseases and ultimately threatens human life. Abnormal blood lipid level is one of the most common diagnostic indicators of AS in clinic, and lipid metabolism disorder is often observed in patients with AS. Cholesterol is an important lipid in the human body, which is of great significance for maintaining normal life activities. Generally, cholesterol is transported to peripheral tissues by low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and then transported to the liver by high-density lipoprotein (HDL) via its cholesterol reverse transport function, and finally discharged. Under oxidative stress condition, LDL is commonly oxidized to the form ox-LDL, which is ingested by macrophages in large quantities and further forms foam cells, disrupting the normal metabolic process of cholesterol. Importantly, the foam cells are involved in forming atherosclerotic plaques, whose rupture may lead to ischemic heart disease or stroke. Furthermore, ox-LDL could also promote the development of AS by damaging vascular endothelium, promoting the migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells, and activating platelets. Therefore, inhibiting LDL oxidation may be an effective way to improve lipid metabolism and prevent AS. In recent years, increasing studies have shown that herbal medicines have great potentiality in inhibiting LDL oxidation and reducing ox-LDL induced foam cell formation. Accordingly, this paper summarized current research on the inhibitory effects of herbal medicines against LDL oxidation and foam cell formation, and made a brief description of the role of cholesterol and LDL in lipid metabolism disorder and AS pathogenesis. Importantly, it is suggested that herbal medicines could inhibit LDL oxidation and regulate cholesterol homeostasis via downregulation of CD36 and SR-A, whereas upregulation of ABCA1 and ABCG1.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; herbal medicines; lipid metabolism; low-density lipoprotein; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2023 Duan, Song, Li, Su and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diterpenoids inhibit ox-LDL-induced foam cell formation in RAW264.7 cells by promoting ABCA1 mediated cholesterol efflux.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 12;14:1066758. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1066758. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36713845 Free PMC article.
-
Inclisiran inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced foam cell formation in Raw264.7 macrophages via activating the PPARγ pathway.Autoimmunity. 2022 Jun;55(4):223-232. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2022.2051142. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Autoimmunity. 2022. PMID: 35289693
-
Guang Chen Pi (the pericarp of Citrus reticulata Blanco's cultivars 'Chachi') inhibits macrophage-derived foam cell formation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;293:115328. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115328. Epub 2022 Apr 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35489660
-
Foam cells in atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:245-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23782937 Review.
-
Effects of curcumin on low-density lipoprotein oxidation: From experimental studies to clinical practice.EXCLI J. 2022 Jun 22;21:840-851. doi: 10.17179/excli2022-4878. eCollection 2022. EXCLI J. 2022. PMID: 36110563 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inulin alleviates atherosclerosis through improving lipid metabolism, inflammation, and gut microbiota in ApoE-knockout mice: the short-chain is more efficacious.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 10;15:1445528. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1445528. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39449970 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Inhibits AGE-Induced NADPH Oxidase-Derived Oxidative Stress Generation and Foam Cell Formation in Macrophages Partly via AMPK Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 8;25(17):9724. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179724. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273671 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of Antioxidant and Anti-Glycation Properties of Beeswax Alcohol in Reconstituted High-Density Lipoprotein: Safeguarding against Carboxymethyllysine Toxicity in Zebrafish.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 14;12(12):2116. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122116. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136235 Free PMC article.
-
AhR, PXR and CAR: From Xenobiotic Receptors to Metabolic Sensors.Cells. 2023 Nov 30;12(23):2752. doi: 10.3390/cells12232752. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of Proteomics in Obesity: Unpacking the Molecular Puzzle.Curr Obes Rep. 2024 Sep;13(3):403-438. doi: 10.1007/s13679-024-00561-4. Epub 2024 May 4. Curr Obes Rep. 2024. PMID: 38703299 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

