Association of diabetes, hypertension, and their combination with basal symptoms and treatment responses in overactive bladder patients
- PMID: 37063295
- PMCID: PMC10097919
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1144470
Association of diabetes, hypertension, and their combination with basal symptoms and treatment responses in overactive bladder patients
Abstract
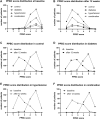
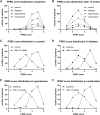
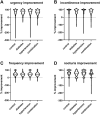
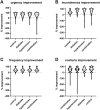
Introduction: Pelvic hypoperfusion caused by atherosclerosis has been proposed as a cause of lower urinary tract dysfunction including overactive bladder syndrome (OAB). Limited data indicate that OAB patients with concomitant diabetes or hypertension, known risk factors of atherosclerosis, may exhibit greater baseline OAB symptoms and slightly smaller therapeutic responses to treatment, but the impact of a combined presence of diabetes and hypertension has not been reported. Therefore, we have explored whether the combined presence of both comorbidities is associated with greater baseline OAB symptoms than that of either comorbidity alone. Secondary questions were exploration of the impact of either comorbidity on baseline symptoms, and of the impact of either comorbidity alone and their combination on therapeutic responses. Methods: Data from two non-interventional studies applying treatment with propiverine ER 30 or 45 mg/d for 12 weeks were analyzed. Results: Number of urgency episodes in the combination group was greater than with each comorbidity alone. The impact of comorbidities on baseline intensity of incontinence, frequency or nocturia or Patient Perception of Bladder Condition was less consistent or absent. Either comorbidity alone was associated with a smaller % improvement of symptoms, and their combination had a greater effect than either alone. However, all attenuations associated with comorbidity were small relative to the overall improvement. Conclusions: We conclude that comorbidities of diabetes and hypertension have detectable effects on OAB symptoms and treatment responses, but the small magnitude of these alterations does not justify changing existing paradigms for the clinical management of OAB.
Keywords: comorbidity; diabetes; hypertension; non-interventional study; overactive bladder syndrome; propiverine; treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Müderrisoglu, Sakul, Murgas, de la Rosette and Michel.
Conflict of interest statement
SM is employed by APOGEPHA Arzneimittel GmbH. MM has been a consultant and/or speaker for Apogepha, Astellas, Dr. Willmar Schwabe and GSK. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Understanding the elements of overactive bladder: questions raised by the EPIC study.BJU Int. 2008 Jun;101(11):1381-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.07573.x. Epub 2008 Mar 10. BJU Int. 2008. PMID: 18336602
-
Can surgical reconstruction of vaginal and ligamentous laxity cure overactive bladder symptoms in women with pelvic organ prolapse?BJU Int. 2019 Mar;123(3):493-510. doi: 10.1111/bju.14453. Epub 2018 Jul 30. BJU Int. 2019. PMID: 29908047
-
Effects of tolterodine ER on patient-reported outcomes in sexually active women with overactive bladder and urgency urinary incontinence.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Sep;25(9):2159-65. doi: 10.1185/03007990903103279. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19601704 Clinical Trial.
-
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in Females and the Overlap with Overactive Bladder.Curr Urol Rep. 2018 Sep 13;19(11):94. doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0839-3. Curr Urol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30215140 Review.
-
Management of OAB in those over age 65.Curr Urol Rep. 2013 Oct;14(5):379-85. doi: 10.1007/s11934-013-0338-5. Curr Urol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23922134 Review.
Cited by
-
Organ-specific off-target effects of Pim/ZIP kinase inhibitors suggest lack of contractile Pim kinase activity in prostate, bladder, and vascular smooth muscle.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Feb;397(2):1219-1231. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02664-6. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37658212 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Blood Lead Levels and Urgency Urinary Incontinence Among Adult Females: A Retrospective Study Based on NHANES 2005-2020.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Jul;203(7):3630-3639. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04445-5. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 39505808
-
Global Prevalence of Overactive Bladder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Int Urogynecol J. 2025 Feb 14. doi: 10.1007/s00192-024-06029-2. Online ahead of print. Int Urogynecol J. 2025. PMID: 39951109 Review.
-
Activation of Hippo/YAP signaling pathway exacerbates vascular remodeling and aggravates hypertension by upregulating Foxm1.J Mol Histol. 2025 May 19;56(3):158. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10443-1. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40388085
References
-
- Amiri M., Schneider T., Oelke M., Murgas S., Michel M. C. (2021). Factors associated with decisions for initial dosing, up-titration of propiverine and treatment outcomes in overactive bladder syndrome patients in a non-interventional setting. J. Clin. Med. 10, 311. 10.3390/jcm10020311 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

