The impact of online office on social anxiety among primary and secondary school teachers-Considering online social support and work intensity
- PMID: 37063568
- PMCID: PMC10101334
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1154460
The impact of online office on social anxiety among primary and secondary school teachers-Considering online social support and work intensity
Abstract
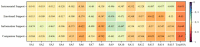
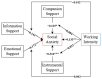
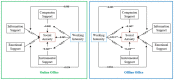
The COVID-19 has had a major impact on the global education system. In order to ensure the normal implementation of education courses, governments and education departments around the world have taken corresponding emergency measures. Based on data from 384 validated questionnaires, this study explored the effects of teleworking practices, work intensity, and online social support on social anxiety among primary and secondary school teachers. The results found that teleworking was more likely to cause social anxiety among teachers, while work intensity could promote social anxiety and online social support could reduce the probability of social anxiety. Work intensity can weaken the influence of partner support on social anxiety. Moreover, the model path coefficients differed across work styles. Based on the results, this study proposes some policy recommendations in order to provide theoretical guidance for improving social anxiety among primary and secondary school teachers and promoting the quality of educational work.
Keywords: equations models; online office; online social support; social anxiety; structural.
Copyright © 2023 Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Teacher Teleworking during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Association between Work Hours, Work-Family Balance and Quality of Life.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 16;18(14):7566. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147566. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34300015 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating stress, anxiety, social support and sex satisfaction on physical education and sports teachers during the COVID-19 pandemic.Heliyon. 2021 Aug 23;7(8):e07860. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07860. eCollection 2021 Aug. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34485739 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of job environment on the online teaching anxiety of college teachers in the online teaching context: The mediating role of subjective well-being.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 14;10:978094. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.978094. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36311626 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated With the Limitation at Work Because of the Voice: Study With Teachers of Basic Education In Brazil.J Voice. 2023 Jan;37(1):79-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2020.11.003. Epub 2020 Nov 17. J Voice. 2023. PMID: 33214005 Review.
-
[What support of young presenting a first psychotic episode, when schooling is being challenged?].Encephale. 2017 Dec;43(6):570-576. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Encephale. 2017. PMID: 29128195 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Social Anxiety among Middle-Aged Teachers in Secondary Education Schools.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2024 Aug 18;14(8):2390-2403. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe14080158. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2024. PMID: 39194952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakker A. B. (2007). The job demands-resources model: state of the art. J. Manag. Psychol. 22, 309–328. doi: 10.1108/02683940710733115 - DOI
-
- Barros A. S. S. (2017). Subjective well-being (Sb) and burnout syndrome (BnS): correlational analysis teleworkers education sector. Procedia. Soc. Behav. Sci. 237, 1012–1018. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2017.02.144 - DOI
-
- Basilaia G., Kvavadze D. (2020). Transition to online education in schools during a SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic in Georgia. Pedagog. Res. 5:1–9. doi: 10.29333/pr/7937 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

