Bridging the Gap Between Believing and Memory Functions
- PMID: 37063695
- PMCID: PMC10103061
- DOI: 10.5964/ejop.7461
Bridging the Gap Between Believing and Memory Functions
Abstract
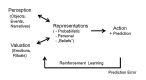
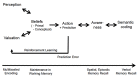
Believing has recently been recognized as a fundamental brain function linking a person's experience with his or her attitude, actions and predictions. In general, believing results from the integration of ambient information with emotions and can be reinforced or modulated in a probabilistic fashion by new experiences. Although these processes occur in the subliminal realm, humans can become aware of what they believe and express it verbally. We explain how believing is interwoven with memory functions in a multifaceted fashion. Linking the typically rapid and adequate reactions of a subject to what he/she believes is enabled by working memory. Perceptions are stored in episodic memory as beneficial or aversive events, while the corresponding verbal descriptions of what somebody believes are stored in semantic memory. After recall from memory of what someone believes, personally relevant information can be communicated to other people. Thus, memory is essential for maintaining what people believe.
Keywords: beliefs; believing; brain; credition; meaning; memory; neural processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Angel, H.-F. (2020). A history of the evolution of religion. From religion to religiosity to the processes of believing. In J. R. Feierman & L. Oviedo. (Eds.), The evolution of religion, religiosity and theology, (pp. 87–103). Routledge.
-
- Angel, H.-F., Oviedo, L., Paloutzian, R. F., Runehov, A. L. C., & Seitz, R. J. (Eds.). (2017). Processes of believing: The acquisition, maintenance, and change in creditions. Springer.
-
- Angel, H.-F., & Seitz, R. J. (2016). Process of believing as fundamental brain function: The concept of credition. SFU Research Bulletin, 4(1), 1–20. 10.15135/2016.4.1.1-20 - DOI
-
- Assmann, A. (2012). Cultural memory and Western civilization. Cambridge University Press.
-
- Assmann, J. (2012). Cultural memory and early civilization. Writing, remembrance, and political imagination. Cambridge University Press. 10.1017/CBO9780511996306 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
